Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
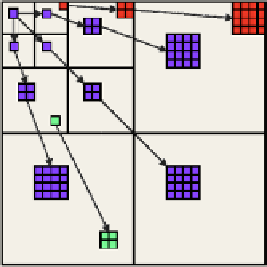
Fig. 5
Location principle in
Daubechies Pyramid
correspondences between a coefficient of the current level and four coefficients at
the lower level.
Then the projected segmentation is refined using motion masks obtained at lower
level and low and high-frequency coefficients contained in the subbands of the cur-
rent level of the pyramid.
Colour segmentation of LL subband at the top of the pyramid is performed by
a known morphological approach. Its application does not really differ from previ-
ously studied morphological segmentation by a simplified watershed adapted to low
resolution version of compressed video frames [11].
It is in the detection of motion masks and refinement of the segmentation across
wavelet pyramid, that the nature of wavelet subbands is truly used. Hence we will
focus on these aspects in the following.
Motion estimation in the Wavelet domain
The problem of motion estimation in the wavelet domain has been extensively stud-
ied for the development of motion-compensated wavelet encoders [26]. Due to the
shift variant nature of DWT, direct band-to-band motion estimation by classical
Block Matching (BM) fails to give sufficiently reliable information when used on
the lower resolution levels, especially for the HF subbands. Several methods have
been developed to limit the effects of the shift-variance of the wavelet transform.
One of the possible approaches was to estimate motion on the LL subband and
motion-compensate HF subbands with the estimated vectors. In order to limit the
shift-variance, the matching is done between the current frame and the translated
versions of the reference frame in wavelet domain [27], other approaches consist
of estimating motion in Overcomplete DWT (ODWT) without sub-sampling [28].
Nevertheless in JPEG2000, the Daubechies pyramid is already imposed by the stan-
dard. Hence for the sake of separation of motion masks from the background motion,
the estimation between the LL subbands of each level of the pyramid and regular-
ization with robust global motion estimation is proposed.
The first step consists in estimating motion vectors on the block-basis on the
lowest
k
−
th
resolution level minimizing “Mean Absolute Difference” criterion in
Eq. (9) when initializing them by zero motion.