Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
if the video player stops displaying the thumbnail video, the transmission of the base
layer can be discontinued.
Coding Slices with Multiple Representations.
Prior work on view random ac-
cess, mentioned in Sect. 2.1 employs multiple representations for coding an image.
Similarly, we can use multiple representations for coding a high-resolution slice.
This will allow us to use interframe coding among successive high-resolution layer
frames and transmit the appropriate representation for a slice depending on the slices
that have been transmitted earlier. For some representations, the MVs can be al-
lowed to point outside slice boundaries. Note that this might lower the transmission
bit-rate but more storage will be required for multiple representations. The benefit
of the scheme in Fig. 2 is that knowing the current RoI is enough to decide which
data need to be transmitted unlike the case of multiple representations where the
decision is conditional on prior transmitted data.
Improvement Based on Background Extraction.
Now let us see how the coding
scheme from Fig. 2 can be improved for higher coding efficiency without employ-
ing multiple representations. Although the coding scheme of Fig. 2 enables efficient
random access, upward prediction using the reconstructed thumbnail frames might
result in substantial residual energy for high spatial frequencies. We propose cre-
ating a background frame [57, 58] for each high-resolution layer and employing
long-term memory motion-compensated prediction (LTM MCP) [59] to exploit the
correlation between this frame and each high-resolution frame to be encoded [60].
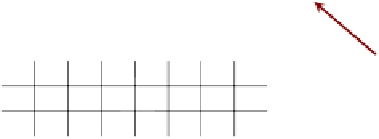
The background frame is intracoded. As shown in Fig. 3, high-resolution P slices
have two references to choose from, upward prediction and the background frame. If
a transmitted high-resolution P slice refers to the background frame, relevant I slices
from the background frame are transmitted only if they have not been transmitted
RoI
Resolution layer n
-
P slices
Upsampled,
reconstructed thumbnail
Rate-distortion
optimized reference
selection
Background frame
I slices
Long-term reference
buffer
Fig. 3
Each high-resolution layer frame has two references to choose from, the frame ob-
tained by upsampling the reconstructed thumbnail frame and the background frame from the
same layer in the background pyramid.