Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
size of the lowest frequency subbands for all 3D holoscopic test images used here
are a multiple of 8×8, which simplifies the computation of the 3D-DCT transform.
Hence blocks of 8×8 pixels from eight successive view point images are grouped
together to form an 8×8×8 volume as input to the 3D-DCT unit. The coefficients
resulting from the application of the 3D-DCT are passed to a Huffman encoder
while all the other coefficients are passed to an arithmetic encoder.
56
w
3
0
2
u
v
1
(a)
(b)
Fig. 10
(a) 2-levels 2D-DWT on viewpoint images, (b) Grouping of the lower frequency
bands into 8×8×8 blocks
5.3 Proposed Compression Algorithm
The 56 extracted viewpoint images are DC level shifted. Then, a forward 1D
DWT is applied on the whole sequence of viewpoint images. This results in 28
low frequency bands and 28 high frequency bands. The same procedure is then re-
peated on the resulting 28 low frequency bands only. This leads to 14 low fre-
quency bands and 14 high frequency bands. The procedure is repeated to the low
frequency bands at each decomposition level until only two low frequency bands
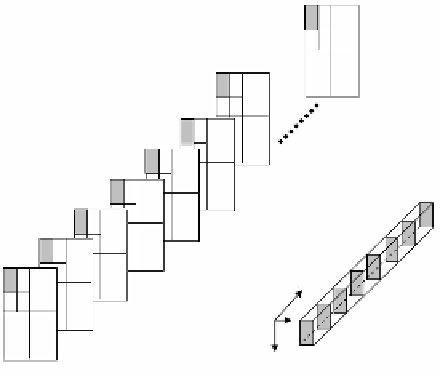
are reached. The procedure is depicted in Figure 11 for five levels of inter-
viewpoint image decomposition. Next, a forward 2-levels 2D DWT on the last two
low frequency bands is carried out. After quantization, all the resulting quantized
samples are Arithmetic encoded. Finally, the decoder undoes all these operations
allowing the reconstruction of the intensity distribution.
Prior to Arithmetic coding, de-correlated sub-image groups resulting from ap-
plication of the spatial decomposition on the last two low frequency bands, are