Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
most multi-view displays, thus enabling more diamond shaped viewing positions
at the expense of invalid zones in between.
Autostereoscopic displays typically use parallax barrier, lenticular sheet or
wavelength selective filter which divide the pixels of the underlying, typically
LCD display into two or more sets corresponding to the multiple directions.
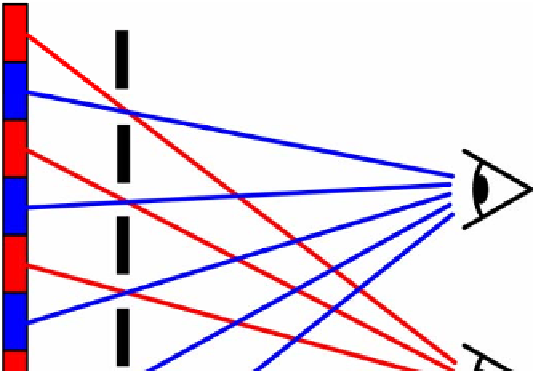
3.1 Parallax Barrier
Parallax barrier [38] is an array of slits spaced at a defined distance from a high
resolution display panel. The parallax effect is created by this lattice of very thin
vertical lines, causing each eye to view only light passing through alternate image
columns, allowing the well-positioned viewer to perceive stereoscopic 3D, as
shown In Fig. 8. Parallax barrier-based displays typically show stereoscopic 3D
made up of two images, but with the proper choice of distance and width of the
slit multi-view effect can be provided. Parallax barrier systems are less efficient in
terms of light output, thus the image gets darker than in 2D, especially in case of
multiple views.
Parallax barrier displays are making their way to mobile devices, as they can be
easily implemented in small size. One example is a 3.07” size WVGA 3D LCD
Fig. 8
Principle of parallax barrier based stereoscopic vision