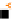Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
W
ROI
z
p
i
2
u
d
i
2
x
CS
y
u
l
i
u
i
H
b
i
2
e
i
E
l
i
E
i
Fig. 2
The viewing geometry
ROI. The preferential positions
E
i
are placed on those lines according to their sec-
ond index
i
2
in order to guarantee that a viewer whose binocular gap is
b
i
2
(often
identical to human medium binocular gap 65 mm, but possibly different according
to the expected public: children, etc.), with the eyes line parallel to the device rows,
would have his right eye in
E
i
and his left eye in
E
l
i
. The right eye in
E
i
would
catch image number
i
, while the left eye in
E
l
i
would catch image number
l
i
know-
ing that
l
i
=
i
(
q
i
2
,
0) with
q
i
2
being the gap between the indexes of images which
compose the visible consistent stereoscopic couples with binocular gap
b
i
2
−
at dis-
tance
d
i
2
. Hence, associated left and right eye preferential positions
E
l
i
and
E
i
verify
E
i
=
E
l
i
+
b
i
2
x
and
e
i
=
e
l
i
+
b
i
2
.
We also define the lines positions vertically (because viewers of various sizes use
the device) by
p
i
2
which represents the “overhang”,
i.e.
, the vertical gap of eyes po-
sitioning compared with the ROI center
CS
. If we don't know
p
i
2
,weuseamedium
overhang corresponding to a viewer of medium size, which has to be chosen at de-
sign stage. Assuming
u
i
and
u
l
i
are stereoscopic homologous for images
i
and
l
i
,
their perception by the right and left eye of a viewer from
E
i
and
E
l
i
leads this spec-
tator's brain to perceive a 3D point
u
. The viewing geometry analysis is expressed
thanks to a global reference frame
r
=(
CS
,
x
,
y
,
z
y
), chosen at the ROI center
CS
, with
x
parallel to its rows and turned towards the right of the spectators, and y
parallel to its columns and turned towards the bottom.
≡
x
×
2.2
Shooting
×
In order to “feed” such devices with 3D content, we need sets of
n
m
images
from a single scene acquired from several distinct and judicious viewpoints and with
specific projective geometry as the rendering upon flat multiscopic devices involves
coplanar mixing of these images. This major issue is well known in multiscopy.
The image viewing is achieved according to distorted pyramids whose com-
mon base corresponds to the device ROI and the tops are the viewer's eyes or