Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
det(
H
i
)
K
(
H
i
)
−
1
H
i
(
x
i
−
x
)
1
K
MASK
(
x
i
−
x
)=
·
K
h
t
(
t
i
−
t
)
det(
H
i
)
K
(
H
i
)
−
1
x
i
m
i
1
(
t
i
t
)
1
=
−
x
−
−
·
K
h
t
(
t
i
−
t
)
exp
=
det(
C
i
)
h
s
h
t
t
)
m
i
1
(
t
i
−
2
1
2
h
s
−
x
i
−
x
−
C
i
exp
2
−
|
t
i
−
t
|
·
(28)
2
h
t
2
C
i
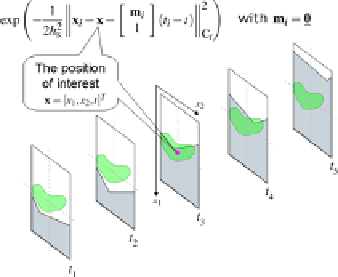
is weighted squared
L
2
-norm. Figs. 5(a-i)-(a-iii) graphically describe
how the proposed MASK function constructs its weights for spatial upscaling. For
ease of explanation, suppose there are 5 frames at times from
t
1
to
t
5
, and we upscale
where
·
(a-i) 2-D steering kernel weights for each frame
(a-ii) Shifting the kernel with local motion vectors
(a-iii) Scaling by the temporal kernel function
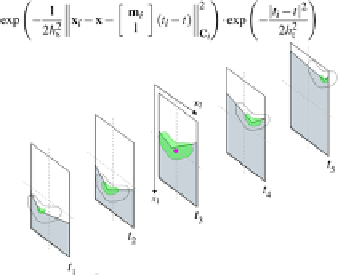
(b) MASK weights for temporal upscaling
Fig. 5
Schematic representations of the construction of MASK weights: the proposed MASK
weights are constructed by the following procedure (a-i) compute 2-D steering kernel weights
for each frame (with
m
i
=
0
at this moment), (a-ii) shift the steering kernels by the local
motion vectors, and (a-iii) scale the shifted steering kernels by the temporal kernel function.
Fig.(b) shows the weight construction for the estimation of an intermediate frame at time
t
.