Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
across two or more pictures is known as Inter prediction. A method of further ex-
ploiting correlation between frames is to utilize motion prediction, which is re-
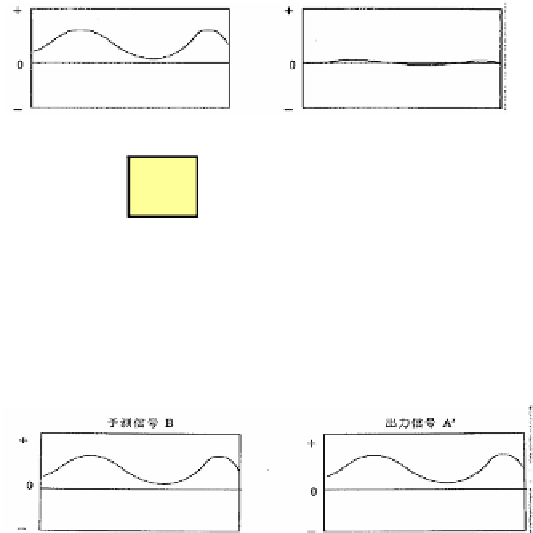
ferred to as Motion Compensated Prediction. Fig. 8 shows the difference of power
between several signals in a typical video coding system.
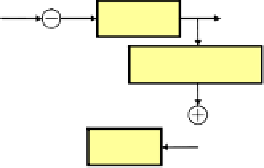
Input picture signal
S
i
Prediction error signal
e
i
ᾌ
S
i
ὼ
P
i
Variable
length
coding
Variable
length
decodin
S
i
e
i
Inverse
quantizer
e
i
'
S
i
'
Quantizer
Inverse quantizer
e
i
'
AR
predictor
AR
predictor
P
i
S
i
'
P
i
Prediction signal
P
i
Decoded picture signal
S
i
'
ᾌ
P
i
ὺ
e
i
'
Fig. 8
Predictive Coding Scheme
3.2.1.1 Intra Frame Prediction
Intra Frame Prediction is a prediction technique that uses the neighboring pixels
within a frame. Three prediction methods including Previous-sample Prediction,
Matrix Prediction and Plane Prediction are shown as examples of Intra Frame Pre-
diction in Fig. 9. Previous-sample Prediction uses neighboring pixels in the hori-
zontal direction as a prediction pixel, Matrix Prediction uses neighboring pixels in
both horizontal and vertical directions, and Plane Prediction uses neighboring pix-
els in horizontal direction and subtracts the pixel values at the same positions on
the former line.
3.2.1.2 Motion Compensated Prediction
Motion Compensated Prediction is a technique which creates a prediction image
that resembles the current image by linear translation of a block within a reference
picture which is already transmitted and decoded. Compression is achieved by