Database Reference
In-Depth Information
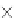
TID Rank Prob.
Top-
k
probabilities
k
=
1
k
=
2
k
=
3
k
=
4
o
1
1
0
.
5
0
.
5
0
.
5
0
.
5
0
.
5
o
2
2
0
.
3
0
.
15
0
.
3
0
.
3
0
.
3
o
3
3
0
.
7
0
.
245
0
.
595
0
.
7
0
.
7
o
4
4
0
.
9
0
.
0945 0
.
45 0
.
8055
0
.
9
Table 2.2
Top-
k
probabilities of a set of tuples.
1
o1
o2
o3
o4
Q2
0.8
0.6
Q3
Q1
0.4
0.2
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
Rank k
Fig. 2.5
Ranking queries on uncertain tuples.
Example 2.8 (PT-k query and Top-
query). Consider a set of uncertain in-
stances in Table 2.2. Suppose each instance belongs to one uncertain object and
all objects are independent. In Figure 2.5, we plot the top-k probabilities of all in-
stances with respect to different values of k.
APT-
3
query with probability threshold p
(
k
,
l
)
=
.
{
,
,
}
0
45
returns instances
o
1
o
3
o
4
whose top-
3
probabilities are at least
0
.
45
. Interestingly, the PT-
3
query with proba-
bility threshold p
in Figure 2.5. As
the answers to the query, the top-k probability curves of o
1
,o
3
and o
4
lie northeast
to Q
1
.
Alternatively, a top-
=
0
.
45
can be represented as a point Q
1
(
3
,
0
.
45
)
,
which have the highest top-
3
probabilities. The query can be represented as a verti-
cal line Q
2
(
k
,
l
)
query with k
=
3
and l
=
2
returns
2
instances
{
o
4
,
o
3
}
in Figure 2.5. The answer set includes the
2
curves which have
the highest intersection points with Q
2
.
(
k
=
3
)
Example 2.9 (RT-k query and Top-
query). Consider the uncertain instances
in Table 2.2 again. An RT-
3
query with probability threshold p
(
p
,
l
)
=
0
.
45
returns
{
. The answer is the same as the answer to the PT-
3
query with the same
probability threshold as shown in Example 2.8.
A top-
o
1
,
o
3
,
o
4
}
(
p
,
l
)
query with p
=
0
.
5
and l
=
2
returns
{
o
1
,
o
3
}
whose
0
.
5
-ranks are the
smallest. The query can be represented as a horizontal line Q
3
in
Figure 2.5. The
2
curves having the leftmost intersections with Q
3
are the answers.
(
probability
=
0
.
5
)