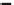Database Reference
In-Depth Information
100
Exact
DLTA
LT3
LT-
tr
ee con
st
ruction
RT
80
200
60
150
40
100
DTLA
LT3
LT-tree construction
20
50
0
0
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
5
10
15
20
25
Neighborhood threshold
Parameter k
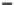
(a) Runtime vs. neighborhood.
(b) Runtime vs.
k
.
400
Exact
LT3
DLTA
LT-tree con
st
ruction
RT
Exact
DLTA
LT-tree construction
LT3
RT
350
1400
300
1200
250
1000
200
800
150
600
100
400
50
200
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
20000
40000
60000
80000 100000
Number of attributes
Number of tuples
(c) Runtime vs. dimensionality.
(d) Runtime vs. cardinality.
Fig. 4.11
Efficiency and scalability of answering top-
k
discriminative typicality queries.
500
2000
DTLA
LT3
LT-tree construction
Exact
DLTA
LT3
LT-tree construction
RT
400
1500
300
1000
200
500
100
0
0
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
5
10
15
20
25
Neighborhood threshold
Parameter k
(a) Runtime vs. neighborhood.
(b) Runtime vs.
k
.
5000
3500
Exact
LT3
DLTA
LT-tree construction
RT
Exact
DLTA
LT-tree construction
LT3
RT
3000
4000
2500
3000
2000
1500
2000
1000
1000
500
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
10000
40000 60000 80000 100000
Number of attributes
Number of tuples
(c) Runtime vs. dimensionality.
(d) Runtime vs. cardinality.
Fig. 4.12
Efficiency and scalability of answering top-
k
representative typicality queries.
we set the neighborhood threshold to 2
h
, where
h
is the bandwidth of the Gaussian
kernel. In such a case, according to Theorem 4.1, the difference between the simple
typicality value and the local simple typicality value of any instance is always less
than 0
05. In the randomized tournament method, by default the tournament group
size is 10 and 4 times validation are conducted. We observe that although with more
.