Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Mucosal folds
Blood capillaries
IMMUNE FATE?:
CD4
+
Th
1
CD4
+
Th
2
CD4
+
Th
17
CD4
+
Treg
Tolerance!
CMI:
Intracellular pathogens
Humoral:
Extracellular pathogens
CMI:
fungal protection
Key:
CD4
+
Theg
CD8
+
Tc / IEL
B cell
slg
Commensal
Pathogen
Defensin
Epithelial cell
M-like cell
Goblet cell
Mucus
DC
Macrophage
CD4
+
Thp
CD4
+
Th
1
CD4
+
Th
2
CD4
+
Th
17
Fig. 2.2
Mucosal immune system of the gut. This figure shows the current understanding that exists for the
gut mucosal immune system of the teleost fish. This tissue exists in folds, but cannot be described as villi due
to the lack of lacteal/lymphatics. The immune defences exist at many levels of the layers of the mucosal
tissue, namely commensal organisms, mucus, epithelial cell layer and sub-epithelial mucosa. Unlike the
mammalian GALT, teleosts do not exhibit Payer's patches or lymphoid follicles. Instead, their lymphoid
tissue is rather diffuse but contains all the immune cells which give the teleost GALT the capability to either
tolerize immune mechanisms (T
reg
) or initiate immune mechanisms directed at the clearance of
intracellular-resident (CD4
+
Th
1
,CD4
+
Th
17
and CD8
+
T
c
) and extracellular-resident pathogens (CD4
+
Th
2
and B cells). One area of controversy in this diagram is the existence of dendritic cells (DCs); it is not
understood whether DCs, specialized macrophages or specialized M-cell-like epithelial cells capable of
antigen transcytosis act as APCs to contextualize MHC-restricted T-cell-driven adaptive immune responses.
Broad-spectrum pathogen defence is associated with barrier function (commensal organisms, mucus
secreted by goblet cells and trapping of sIg-bound pathogens, intact tight junctions and epithelial cell
secretion of anti-microbial products such as defensins) and innate immune responses (macrophage and
granulocyte activity mediated by cytokines and anti-microbial compounds). Through the induction of
expression of teleost cytokine homologues, immune responses can be directed towards the desired effector
response to pathogens and non-pathogens. Such teleost cytokines include TGF
β
and IL-10 (T
reg
), IL-12 (Th
1
),
IL-4 (Th
2
) and IL-23 (Th
17
), thus directing mechanisms of mucosal tolerance, cell-mediated immunity,
humoral immunity and anti-fungal responses, respectively. For colour detail see Plate 6.






























































































































































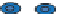


















































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search