Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
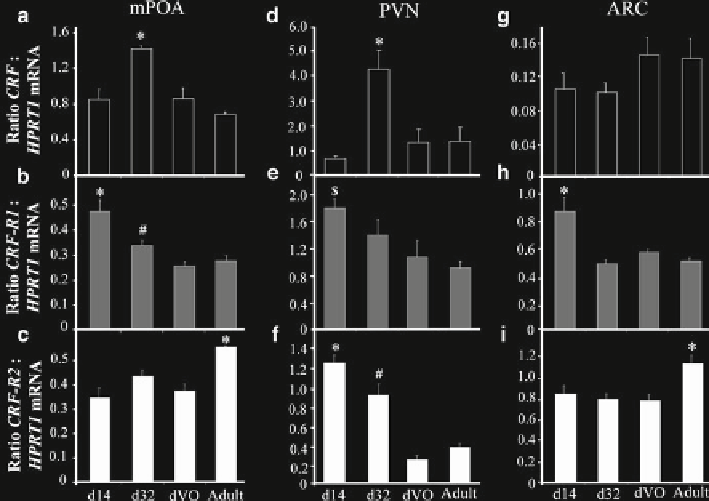
Fig. 20.2
Developmental changes in CRF, CRF-R1, and CRF-R2 across puberty in the medial
preoptic area (mPOA) (
a
-
c
), hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) (
d
-
f
respectively), and
arcuate nucleus (ARC) (
g
-
i
respectively). Time points include postnatal day 14 (d14), 32 (d32),
day of vaginal opening (dVO: 40.9 ± 0.9 days, mean ± SEM), and adult (postnatal day 77).
CRF
,
CRF
-
R1,
and
CRF
-
R2
mRNA levels were measured in brain micropunch samples from the mPOA,
PVN, and ARC using a real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Note the peak
in
CRF
mRNA levels in the mPOA and PVN in the late prepubertal phase that has receded by the
time of puberty and the gradual decline in
CRF
-
R1
expression in the mPOA across the pubertal
transition. Quantifi cation for
CRF
,
CRF
-
R1
,
CRF
-
R2,
and
HPRT1
mRNA was carried out on all
samples and the values are expressed as a ratio of
CRF
,
CRF
-
R1,
or
CRF
-
R2
to
HPRT1
mRNA
(mean ± SEM). *
P
< 0.05 vs. other time points;
#
P
< 0.05 vs. dVO;
$
P < 0.05 vs. adult;
n
= 6-10 per
group (from Kinsey-Jones JS, Li XF, Knox AM, Lin YS, Milligan SR, Lightman SL, et al.
Corticotrophin-releasing factor alters the timing of puberty in the female rat. J Neuroendocrinol.
2010 Feb;22(2):102-9. Reprinted with permission from John Wiley & Sons)
HPA axis by kisspeptin, as proposed by Rao and colleagues [
53
]. Indeed, the inverse
relationship between PVN CRF and mPOA
Kiss1
expression across the pubertal
transition in the female rat (Figs.
20.1
and
20.2
) is striking, though causality is
unknown. In conclusion, a variety of stressors impact on pubertal timing, poten-
tially by interfering with hypothalamic kisspeptin/Kiss1r signaling, though further
research is required to elucidate the neural mechanisms involved in this interaction.
The dynamics of pubertal development constitute a powerful correlate of HPG axis
function vulnerable to stress, and the wealth of evidence for the involvement of
kisspeptin makes the developing reproductive system a useful tool for the study of
interactions between stress and kisspeptin signaling.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search