Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
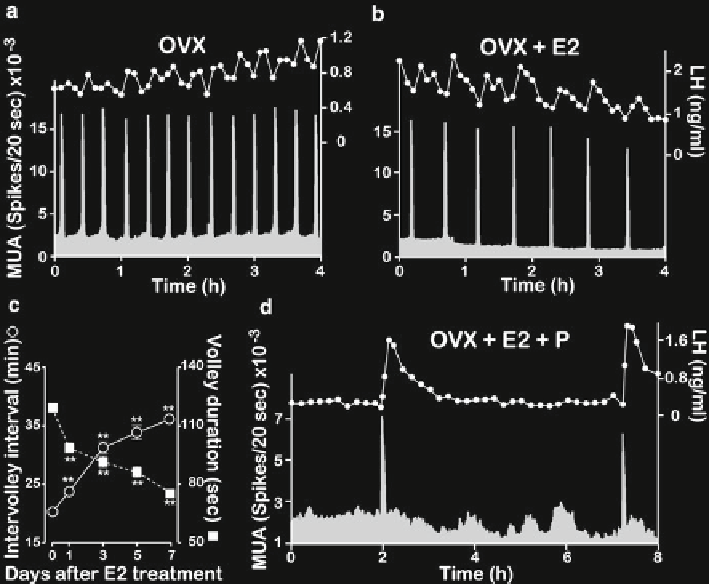
Fig. 14.2
Effects of ovarian steroids on the MUA and LH secretion. (
a
) Representative profi les of
the MUA and plasma LH concentrations in an OVX goat. (
b
) Representative profi les of the MUA
and plasma LH concentrations in an E2-treated OVX goat. (
c
) Changes in the intervolley interval
(
blank circle
) and volley duration (
solid square
) of the MUA volley after the E2 treatment. Data
were collected for 6 h (12:00-18:00) in each day, and values are expressed as mean ± SEM in three
goats. **
p
<0.01 compared with those on Day 0. (
d
) Representative profi les of the MUA and
plasma LH concentrations in an E2 plus P-treated OVX goat. Note that the MUA volley is invari-
ably accompanied by an LH pulse, regardless of the steroidal milieu. Panel (
d
) was reproduced
from Wakabayashi Y, et al. Neurokinin B and dynorphin A in kisspeptin neurons of the arcuate
nucleus participate in generation of periodic oscillation of neural activity driving pulsatile
gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion in the goat. J Neurosci. 2010 Feb 24;30(8):3124-32.
With permission from
Journal of Neuroscience
Using the ovine model, Goodman et al. [
56
] were the fi rst to document that
kisspeptin neurons in the ARC co-express neurokinin B (NKB) and dynorphin
A (Dyn). Since then, the colocalization of kisspeptin with either NKB or Dyn—or
both—in ARC neurons was identifi ed in a variety of mammals, including mice
[
57
,
58
], rats [
59
], goats [
53
], monkeys [
60
], and humans [
61
]. Therefore, concomitant
expression of these three peptides in single ARC neurons appears to be a common
feature across mammalian species. Those neurons, therefore, have been referred to
as KNDy ( kisspeptin/
N
KB/
Dy
n) neurons [
62
].
Search WWH ::

Custom Search