Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
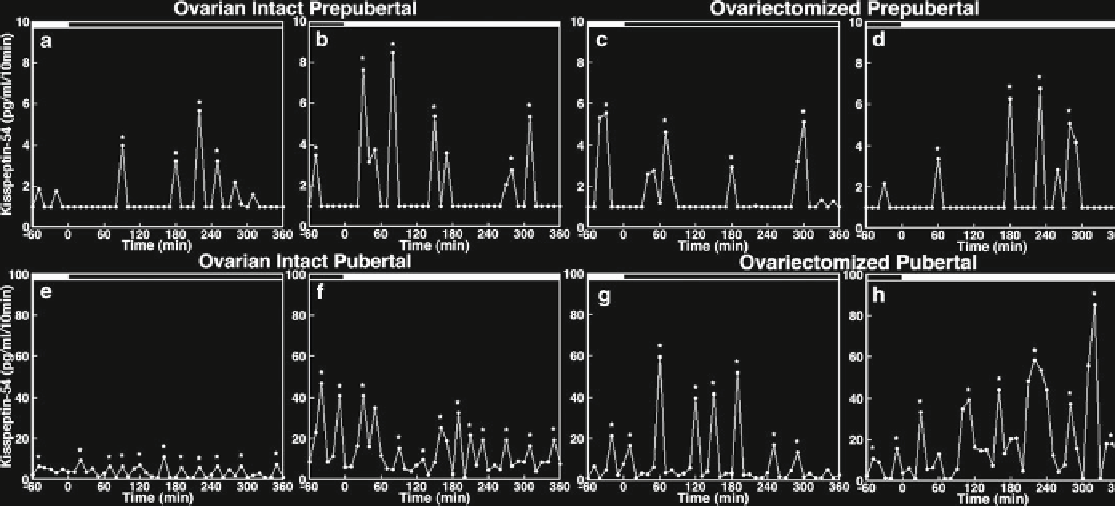
Fig. 12.1
Developmental increases in kisspeptin-54 (KP-54) release are independent of the presence or absence of the ovary in female monkeys. In vivo KP-54
release from the S-ME of ovarian intact prepubertal (
a
,
b
) and pubertal (
e
,
f
) monkeys as well as ovariectomized prepubertal (
c
,
d
) and pubertal (
g
,
h
) monkeys
are shown. Samples were obtained during the morning period (
a
,
c
,
e
,
g
) and during the evening period (
b
,
d
,
f
,
h
) as indicated by the
open
and
closed bars
,
respectively, at the
top
of each graph. Both pulse frequency and amplitude of KP-54 release in ovarian intact pubertal monkeys (
e
,
f
) are higher than those in
ovarian intact prepubertal monkeys (
a
,
b
). Similarly, pulse frequency and amplitude of KP-54 release in ovariectomized pubertal monkeys (
g
,
h
) are higher than
those in ovariectomized prepubertal monkeys (
a
,
b
). Importantly, ovariectomy does not cause any change in KP-54 release ((
a
,
b
) vs. (
c
,
d
)) in prepubertal
monkeys, whereas ovariectomy increases the pulse amplitude of KP-54 release in pubertal monkeys ((
e
,
f
) vs. (
g
,
h
)).
Asterisks
indicate peaks as determined
by PULSAR. Note that the scale of the
y
-axis in (
e
-
h
) (pubertal monkeys) is tenfold higher than that in (
a
-
d
) (prepubertal monkeys). From Guerriero KA, Keen
KL, Terasawa E. Developmental increase in kisspeptin-54 in vivo is independent of the pubertal increase in estradiol in female rhesus monkeys (
Macaca
Search WWH ::

Custom Search