Database Reference
In-Depth Information
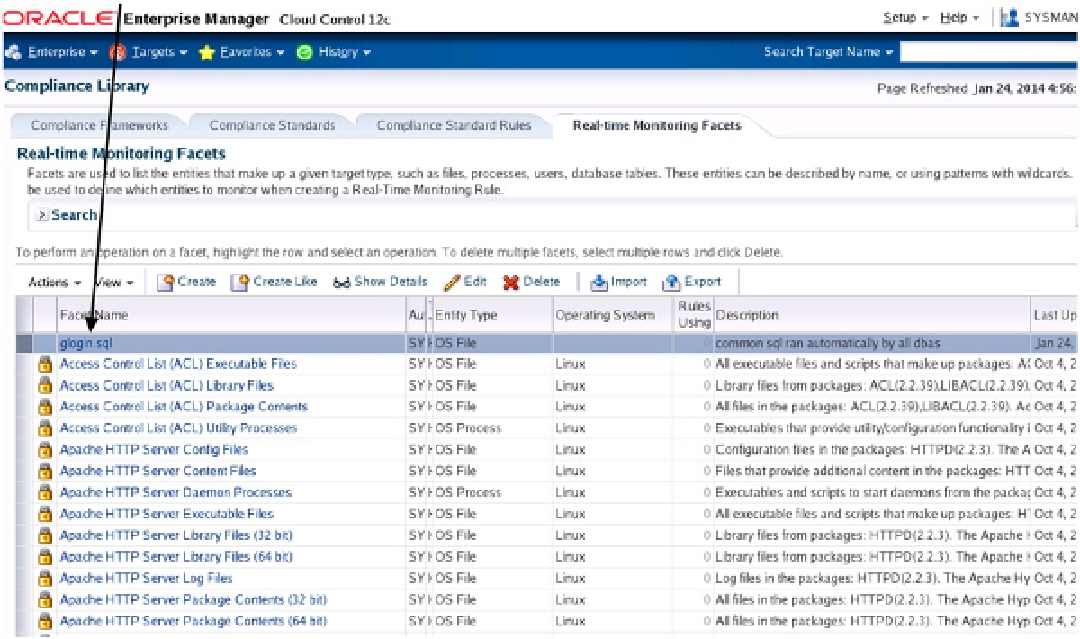
glogin.sql
is now added as a real-time monitoring facet as shown in the output in Figure
17-36
.
Figure 17-36.
glogin.sql
added to the already present facets
glogin.sql
checksum can now be verified automatically by EM Grid Control 12c for the whole estate. The same can
be done for the password file, the wallets, and all the OS files identified in the previous chapters as being foundational
to the security of the Oracle database. The beauty of using EM is that it is easier to push that standard policy out to the
whole estate and to produce reports for different teams, namely DBAs, security team, managers, and auditors.
Of course, this check depends on having the ability to run commands as
"oracle"
*nix from EM, and the other
facets will require root access such as
/etc/shadow
state-checking, so the question here is why are we using these OS
creds in a DBA tool?
Is EM the right place from which to do DB security as it is intrinsically controlled by DBA privilege? The DB needs
to be secured by the OS admin account. That OS admin account should not be stored in EM under the control of the
DBA privilege.
We should have a separate OS category of EM user: the Oracle SA team. This division is beginning to happen in
some organizations, but in most EM is regarded as the DBA-only tool.
The other strategy is to implement access control on the EM12c privileged access account so that EM OS access
is strictly controlled. Privileged access control in EM12c and the cloud is an important subject in chapter 19. First, let's
look at EM12c reports.
EM12c Reports
EM12c reports are moving over to the BI style of report in the long term (see Figure
17-37
). The padlock on the right
shows that SYSMAN owns the prepared reports and that they are locked (i.e., fixed).