Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
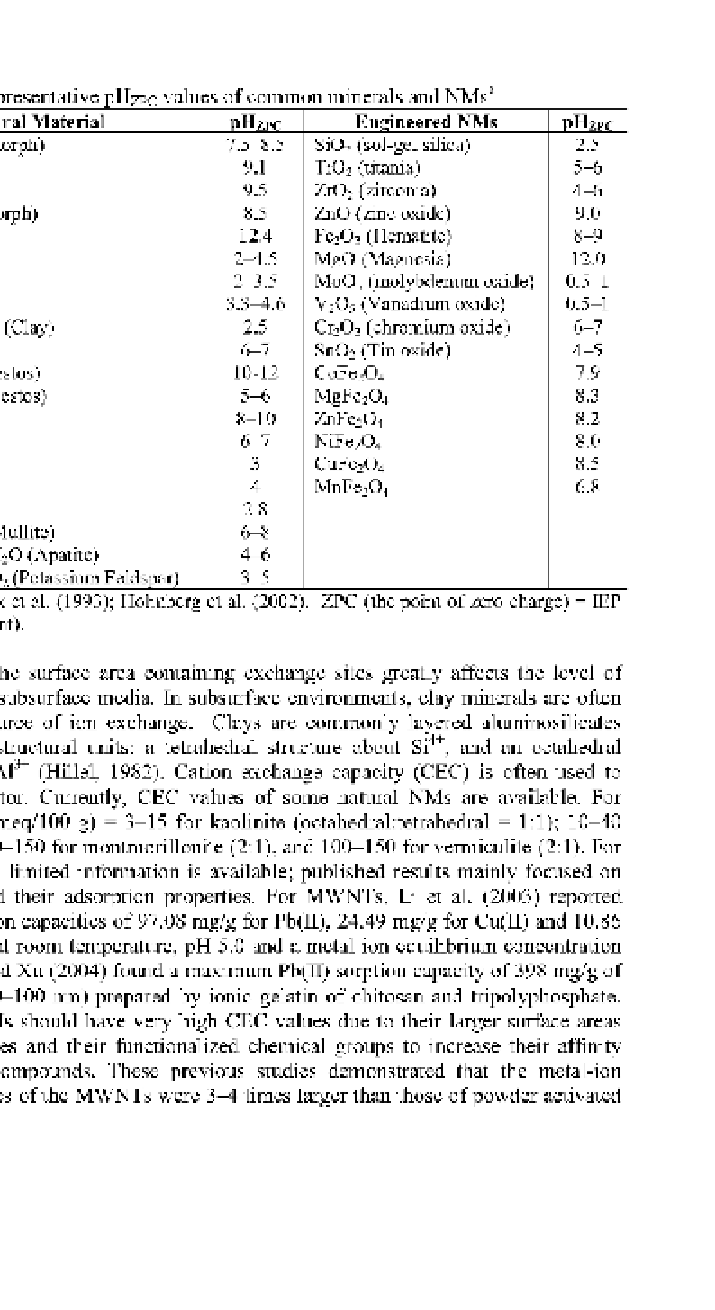
Table 15.11 Representative pHzpc values of common minerals and NMs
a
.
Natural Material
"AL(OH)
3
" (Amorph)
Engineered NMs
SiO
2
(sol-gel silica)
TiO
2
(titania)
ZrO
2
(zirconia)
ZnO (zinc oxide)
Fe
2
O
3
(Hematite)
MgO (Magnesia)
MoO
3
(molybdenum oxide)
V
2
O
5
(Vanadium oxide)
Cr
2
O
3
(chromium oxide)
SnO
2
(Tin oxide)
CoFe
2
O
4
MgFe
2
O
4
ZnFe
2
O
4
NiFe
2
O
4
CuFe
2
O
4
MnFe
2
O
4
pHzpc
7.5-8.5
9.1
9.5
8.5
12.4
2^.5
2-3.5
3.3^.6
2.5
6-7
10-12
5-6
8-10
6-7
3
4
2.8
6-8
4-6
3-5
pHzpc
2.5
5-6
4-6
9.0
8-9
12.0
0.5-1
0.5-1
6-7
4-5
7.9
8.3
8.2
8.0
8.5
6.8
"Fe(OH)
3
" (Amorph)
Montmorillonite (Clay)
Chrysotile (Asbestos)
Crocidolite (Asbestos)
3Al
2
O
3
'2SiO
2
(Mullite)
10CaO6PO
2
.2H
2
O (Apatite)
K
2
OAl
2
O
3
.6SiO
2
(Potassium Feldspar)
a
References: Knox et al. (1993); Holmberg et al. (2002). ZPC (the point of zero charge) = IEP
(the isoelectric point).
Second, the surface area containing exchange sites greatly affects the level of
adsorption for a subsurface media. In subsurface environments, clay minerals are often
the dominant source of ion exchange. Clays are commonly layered aluminosilicates
with two basic structural units: a tetrahedral structure about Si
4+
, and an octahedral
structure about A1
3
+
(Hillel, 1982). Cation exchange capacity (CEC) is often used to
describe this factor. Currently, CEC values of some natural NMs are available. For
example, CEC (meq/100 g) = 3-15 for kaolinite (octahedral:tetrahedral = 1:1); 10-40
for illite (2:1), 80-150 for montmorillonite (2:1), and 100-150 for vermiculite (2:1). For
engineered NMs, limited information is available; published results mainly focused on
nanosorbents and their adsorption properties. For MWNTs, Li et al. (2003) reported
maximum sorption capacities of 97.08 mg/g for Pb(II), 24.49 mg/g for Cu(II) and 10.86
mg/g for Cd(II) at room temperature, pH 5.0 and a metal ion equilibrium concentration
of 10 mg/1. Qi and Xu (2004) found a maximum Pb(II) sorption capacity of 398 mg/g of
chitosan NPs (40-100 nm) prepared by ionic gelatin of chitosan and tripolyphosphate.
By intuition, NMs should have very high CEC values due to their larger surface areas
than bulk particles and their functionalized chemical groups to increase their affinity
towards target compounds. These previous studies demonstrated that the metal-ion
sorption capacities of the MWNTs were
3^
times larger than those of powder activated
Search WWH ::

Custom Search