Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
systems is very important in order to know the behavior and characteristics of these
materials in groundwater aquifers. Recently, we have studied the transport of S-INPs in
a 2-D tank system packed with glass beads and found that there is density effect by
which the S-INPs travels diagonally without significant retardation compared to the
tracer. There should be more research in testing different mobile NPM in 2- and 3-D
systems.
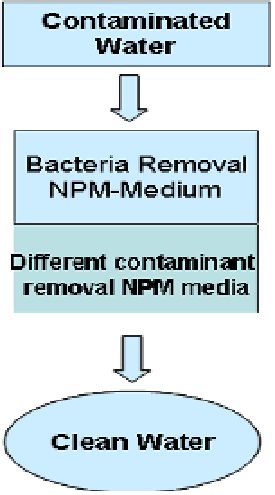
Figure 11.15
Schematic of a composite nanomaterial packed-bed reactor for purification
of water contaminated by mixtures of contaminants (metal ions, organic solutes and
bacteria).
Nanoscale porous materials (NPM) are one of the fastest developing fields. NPM
have a number of key physico-chemical properties, such as high surface area, reactivity,
optical and magnetic properties, oxidation and reduction capacities, etc., that make NPM
attractive for water purification. Development of porous materials such as microporous
zeolites, excellent catalysts and adsorbents for removing multiple contaminants
(organics, inorganics, and heavy metals) shows that these materials are promising novel
technologies. Development of mesoporous silica and alumina made it possible to
Search WWH ::

Custom Search