Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
steps. The technologies have been demonstrated to be economical for large water
treatment systems. Coagulation direct filtration and coagulation microfiltration
technologies eliminate the sedimentation basins and require a much smaller footprint
area than the conventional coagulation filtration processes. These technologies are viable
for applications in small water treatment systems if the suspension generated in the
backwash can be discharged or accepted by a publicly owned treatment works (POTW).
However, it is usually difficult to get a permit for discharging the suspension into a
municipal sewer system even if the suspension is not hazardous material. The costs
associated with handling and disposal of the backwash suspension will be prohibitively
high for small water treatment systems.
H
2
AsO
3
-
H
3
AsO
3
H
2
AsO
4
-
HAsO
4
2
-
100
100
80
80
60
60
40
40
20
20
0
0
02468 0 2 4
pH
02468 0 2 4
pH
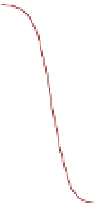
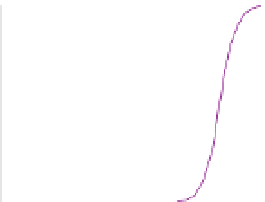
Arsenate, As(V)
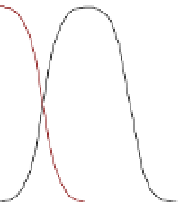
Arsenite, As(III)
100
100
80
80
60
60
40
40
20
20
0
0
0 2 4 6 8 0 2 4
pH
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
pH
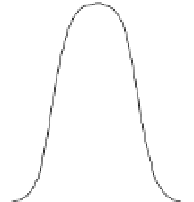
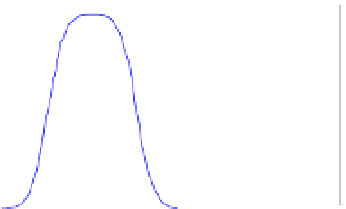
Monomethylarsonic acid, MMA
Dimethylarsinic acid, DMA
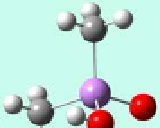
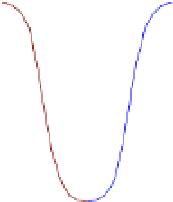
Figure 5.1
Aqueous arsenic speciation as a function of pH. The insertion shows the
molecular structure of protonated species (purple: arsenic, red: oxygen, grey: carbon,
light grey: hydrogen).



































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search