Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
with 59.3% surface area of Au nanoparticles covered by 12.7% of Pd metal content. At
this composition of bimetallic palladium nanoparticles supported on gold nanoparticles
complete TCE degradation were obtained and 90% of the final TCE dechlorination
product was ethane. These results demonstrated that bimetallic palladium nanoparticles
supported on gold nanoparticles have a high potential application in TCE reduction for
groundwater remediation.
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
3,3',4,4'-tetrachlorobiphenyl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
3,3',4-trichlorobiphenyl
3,4,4'-trichlorobiphenyl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
3,3'-dichlorobiphenyl
3,4'-dichlorobiphenyl
4,4'-dichlorobiphenyl
3,4-dichlorobiphenyl
Cl
Cl
4-chlorobiphenyl
3-chlorobiphenyl
biphenyl
Figure 4.3
Possible stepwise degradation of 3,3',4,4'-tetrachlorobiphenyl (BZ# 77) by
microscale ZVI (adapted from Yak et al., 2000).
Degradation of chlorinated aromatic compounds by other metallic nanoparticles
has also shown promising results. Recently, dechlorination of PCBs on Zn/Pd was
investigated and compared against Fe/Pd (Kim et al., 2004). Mono CBs including 2-,3-
and 4-CB were not dechlorinated by plain Zn. A bimetallic system containing Zn/Pd,
however, readily dechlorinated these PCBs at a temperature of 23-25
o
C, with efficiency
even higher than that of the Fe/Pd system (the Pd content of 0.05% weight, Fig. 4.4).
A Mg/Pd bimetallic system was also found to be capable of dechlorinating PCBs
effectively (Agarwal et al., 2007). Mg/Pd particles were synthesized by a wet chemical
method that resulted in nanostructures of Pd depositing on the Mg surface. The Pd
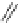










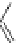






























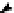


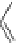












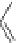


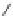


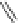



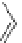


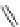
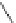

































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search