Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
)[1]withX
itemset and Y itemset are generated by the algorithm APRIORI [1].
The interestingness value of an association rule is calculated via a function
m
with the parameters
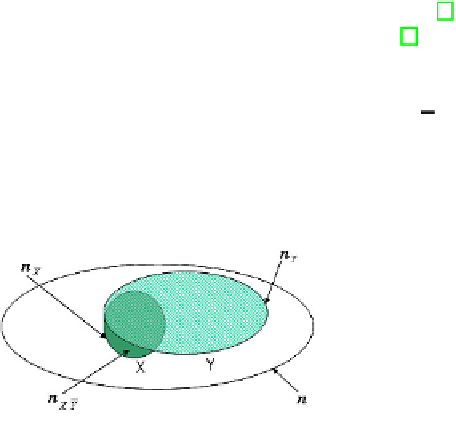
n, n
X
,n
y
,n
XY
(see Fig.1). In this case, the funtion
m
is called an interestingness measure
m
(
X → Y
)=
f
(
n, n
X
,n
Y
,n
XY
) on asso-
ciation rules. The importance of an association rule depends strongly on the
interestingness value that it can obtain from the corresponding interestingness
measure.
An association rule is represented in the form
X → Y
(
X ∩ Y
=
∅
Fig. 1.
Venn diagram for an association rule
X
→
Y
.
3
Interaction between Interestingness Measures
3.1
Interaction Value
The interaction value between two interestingness measures is calculated by a
capacity function (i.e., a fuzzy measure, a measure of capacity) [2] [3] [4]. The
capacity function
μ
on a set
Θ
of interestingness measures
μ
:2
Q
→
[0
,
1] with
the following axioms [2] [9]:
-
μ
(
∅
)=0and
μ
(
Q
) = 1 (normalization).
-
μ
(
A
)
<μ
(
B
)when
A ⊆ B ⊆Q
(monotonicity)
The value
μ
(
A
) demonstrates the capacity of a subset A of interestingness mea-
sures. A capacity function Sugeno [9] or called a capacity with the parameter
λ
(
λ
-measure), if exists a value
λ>−
1sothat:
μ
(
A ∪ B
)=
μ
(
A
)+
μ
(
B
)+
λμ
(
A
)
μ
(
B
)
(1)
with
A ⊆QandA ⊆Q
.
The capacity function Sugeno can be determined by the method ”Singleton
Fuzzy Measure Ratio Standard” [10]. When the function
μ
does not carry on
the additive property (
μ
(
A ∪ B
)
=
μ
(
A
)+
μ
(
B
)) we have :
q
1+
λ
=
(1 +
λμ
(
x
i
))
(2)
i
=1
with :
q
=
|Q|
.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search