Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
the pairwise similarity for erecting the co-association matrix. Each entry of the co-
association matrix according to definition of the novel method which is called
Extended Evidence Accumulation Clustering method, EEAC is as equation 6.
n
i
,
j
C
(
i
,
j
)
=
(6)
max(
n
,
nj
)
i
Where
n
i
and
n
j
are the number of presence in selected clusters for the
i
-th and
j
-th
objects, respectively. Also,
n
ij
counts the number of selected clusters which are shared
by objects with indices
i
and
j.
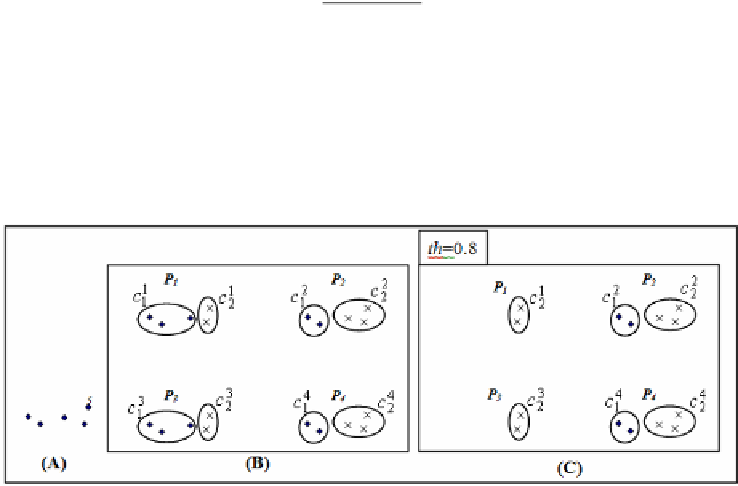
To more explain consider the following example. Assume that 5 samples according
to Fig. 7a, which 4 primary clusterings
P
1
to
P
4
are applied on this data (according to
Fig. 7b).
Fig. 7.
Computing the co-association matrix by EEAC method. (A) Data samples. (B) 4
primary clusterings. (C) Reminded clusters after applying threshold,
th
=0.8.
Also, consider that that stability of the clusters of Fig. 7b is as below:
1
2
3
2
Stability
(
c
)
=
Stability
(
c
)
=
1
1
2
1
4
1
Stability
(
c
)
=
Stability
(
c
)
=
2
2
4
2
Stability
(
c
)
=
Stability
(
c
)
=
0
.
82
1
1
3
1
Stability
By choosing
th
=0.8 the first clusters from
P
1
and
P
3
are deleted (Fig. 7c).
According to equation 6, each entry of co-association matrix is
(
c
)
=
Stability
(
c
)
=
0
55
2
2
C
(
2
=
=
=
1
max(
2
2
)
2
0
0
C
(
=
C
(
2
=
=
=
0
max(
2
2
)
2
2
2
C
(
4
)
=
C
(
=
=
=
0
.
5
max(
2
4
4
4
4
C
(
4
=
=
=
1
max(
4
4
4




Search WWH ::

Custom Search