Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
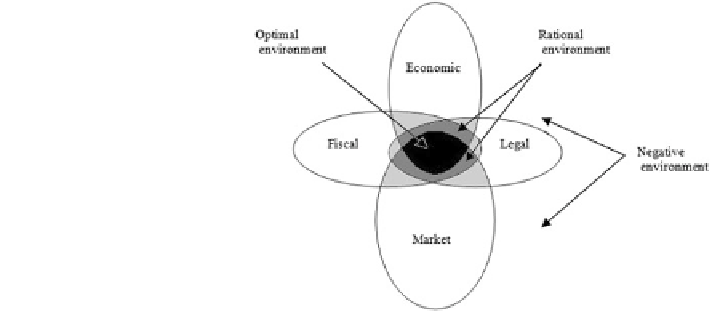
Fig. 4 Determination of
optimal, rational and negative
environment for the built
environment
area (taking into account the significance of the factors), the greater will be the
efficiency level of the built environment. Having investigated the effects of the
micro, meso and macro variables affecting built environment by using best prac-
tices, differences have been identified between these and specific country. On the
basis of these differences, the main implications for specific country can be
identified. Studying only some worldwide experience, knowledge and best prac-
tices could lead to any inferences being purely subjective. However, by studying a
number of countries any bias can be diminished. In other words, the presence of
specific micro-, meso- and macro-level variable factors immediately imposes
objective limitations on the efficient activities of stakeholders. The stakeholders, in
the presence of these objective limitations, try to perform their activities in a more
rational way.
Based on the above considerations, it is possible to propose a Model of Built
Environment Life Cycle Process for Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation on
the basis of the performed search for a rational variable environment for specific
country (i.e. seek to explore ways of harmonising the relationship between the
specific country built environment and its micro, meso and macro environment).
Upon completion of such a model, the stakeholders by taking into consideration
existing limitations of micro-, meso- and macro-level environment and existing
possibilities will be able to use their resources in a more rational manner.
One of the major tasks of an organisation is to carry out its activities under the
most favourable micro-, meso- and macro-level conditions. Efforts are made to
ensure that the structure, goals, output, efficiency and quality of production of the
organisation would be in maximum conformity with the existing environmental
conditions. The pursuit of impracticable goals, for instance, trying to realise
projects that surpass the organisation's capabilities or the environment (econom-
ical, social, legal, political, competitive and technological conditions) is adverse,
may cause undesirable consequences.