Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
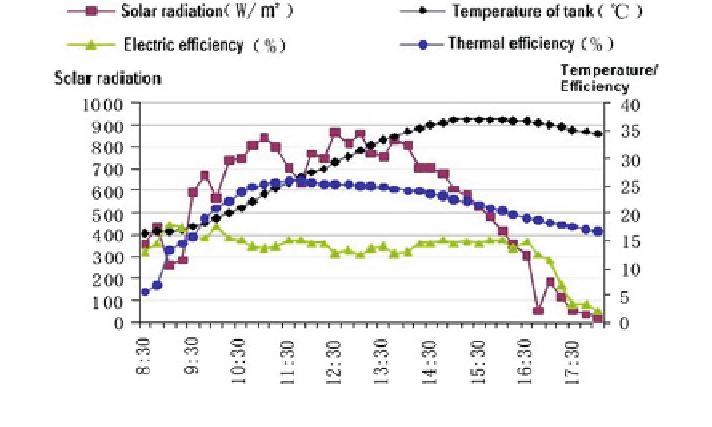
Fig. 24
Variation in daily test efficiency with running time (Zhang et al.
2012
)
optimising heat pipes' geometrical shape sizes and (3) suggesting the configuration
of the integrated PV/T and heat pipe and other heat-removing system including
panel configuration, e.g. covers, PV cells and combination between PVs and heat
pipes and connection between PV/T panels and secondary fluid cycle.
Compared to the refrigerant-based system, the heat-pipe-based system could
achieve an instant equivalent performance if the heat pipes operate at an adequate
temperature. This system may overcome the difficulties existing in the refrigerant-
based system and become the next-generation technology for removing heat from
PVs and effectively utilizing this part of heat. However, this type of system also
found some disadvantages that require further resolutions, e.g. high cost of the heat
pipes and good control of the heat pipe performance.
3.3.2 Analysis of the Research Achievements in Terms
of Research Methodology
In terms of research methodology used, the research works can be classified as (1)
theoretical analysis and computer modelling; (2) experimental study; (3) combined
modelling and experimental study; (4) economic and environmental analysis; and
(5) demonstration of the technology and the associated feasibility study.
Theoretical Analysis and Computer Modelling
Many theoretical works have been carried out to study the performance of the PV/
T modules and the associated heat and power system. These works were dedicated
to (1) reveal the temperature distribution across the various layers of the PV/T
modules and energy (heat and power) conversion mechanism; (2) optimise the