Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
with the air-based system lies in its relatively poor heat-removal effectiveness
owing to the low density, specific heat capacity and thermal conductivity of the air.
Water-based PV/T
Water-based PV/T is secondary popular PV cooling approach, which has gained
growing application in practice over recent years. Numerous commercial products
have emerged on markets, and most impressive examples include 'PVTWIN'
series products by PVTWINS and 'MULTI SOLAR' by Millennium Electric. The
performance of the water-based PV/T technology is usually indicated by its
electrical and thermal efficiencies which are found to vary with the water tem-
perature, flow rate, water flow channel's geometry and sizes, PV type, as well as
external climatic conditions. The most favourite unit configuration and material
are the PV/T laminate with the single-glazing and sheet-and-tube absorber in an
aluminium frame and insulation on the back side, which is regarded as the most
promising design as it has relatively high overall efficiency and is easy to construct
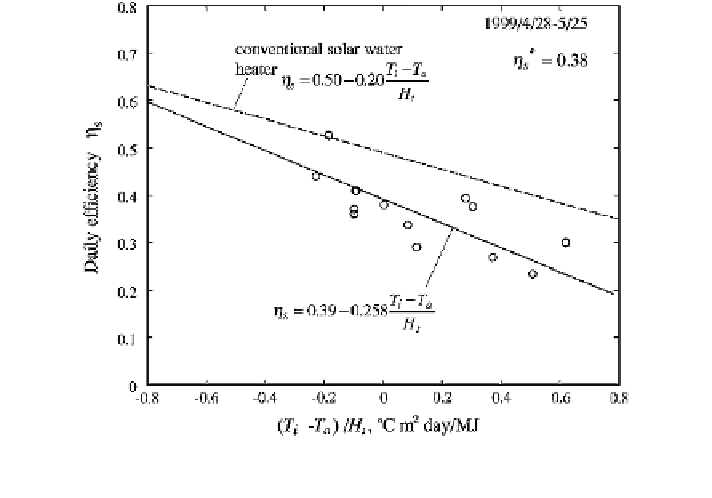
(PVTWINS 2010). A diagram showing correlation between solar efficiencies and
the operational parameters is presented in Fig.
22
(Huang et al.
2001
), which is
established on the basis of the fixed geometrical conditions and PV type.
In overall, a typical water-based PV/T type can achieve maximum electrical
efficiency of around 9.5 % and thermal efficiency of around 50 % (Huang
et al.
2001
). Its performance is largely dependent on water temperature, flow rate,
water flow channel's geometry and sizes, PV type, as well as external climatic
conditions. Researches related to water-based PV/T system usually focus on (1)
determining appropriate water flow velocity and temperature, (2) optimising water
Fig. 22 Daily efficiency test results of integrated PV/T system (Huang et al.
2001
)(H
t
daily total
solar radiation; g
s
characteristic efficiency; T
i
initial temperature of tank water)