Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
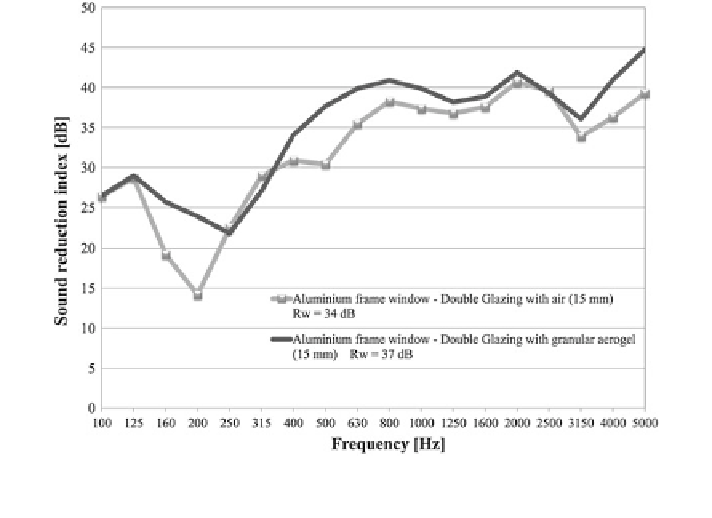
Fig. 7 Sound reduction index (R) values versus frequency for aluminium frame window with
conventional glazing (15-mm air) and with glazing prototype with aerogel in interspace (15 mm)
(R, EN ISO 20140-2
2010
), which affects the noise transmitted through the win-
dows; high values are required in order to guarantee an adequate acoustic comfort
in buildings. The presence of granular aerogel increases the sound reduction index
values in all the frequency range (100-500 Hz), especially in the central range
(500-2,000 Hz). Moreover, a weighted sound insulation index R
w
(EN ISO 717-1
2007
) equal to 37 dB was obtained for the innovative prototype, 3 dB higher than
the one of the conventional window with air in interspace (R
w
= 34 dB), con-
firming good acoustic insulation properties (Fig.
7
).
4 Aerogel Windows
4.1 Glazing Systems
Many innovative glazing technologies were developed in order to satisfy the
growing demand for energy-efficient buildings (Jelle et al.
2012
; Ebrahimpour and
Maerefat
2011
; Wong et al.
2007
); in this context, the current focus is to develop
super-insulating windows, with U-values below 1 W/m
2
K, high light transmis-
sion, and not too high g-value (solar heat gain coefficient). Silica aerogels, both in
monolithic and granular form, can be used in high-insulated nanogel windows,
thanks to their interesting optical properties and excellent thermal insulation
characteristics. Transparent monolithic panes were developed in 1980-1990s