Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Aerogel was discovered by Kistler 80 years ago (Kistler
1931
), and it is a dried
gel often obtained by means of a very complex synthesis in supercritical drying
conditions. The obtained structure (a cross-linked internal structure of silicon
dioxide (SiO
2
) chains and a large number of very small air-filled pores) is extremely
light with significant physical, thermal, optical, and acoustic properties, depending
on both the silica source and the preparation process. Aerogel has the lowest
thermal conductivity among solid materials (down to 0.010 W/m K at room
temperature, depending on the pressure).
Aerogels are applied in several fields (Akimov
2003
; Baetens et al.
2011
;
Aegenter et al.
2011
; Pierre and Pajonk
2002
): microelectronics, electrical engi-
neering, acoustics, oil and gas pipelines insulation, and finally space exploration
(aerogel is in fact used as thermal insulation material in US spacecrafts). More-
over, because of the extraordinary properties, nowadays, aerogels are the most
promising materials in the market of building insulation. In this field, different
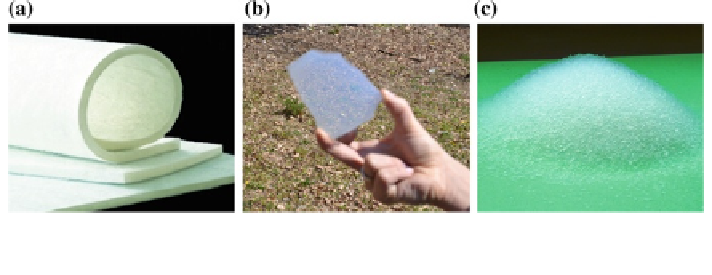
types of aerogels were developed (Fig.
2
):
1. opaque aerogels, such as aerogel blankets, that could be used to reduce thermal
bridges in the building envelope, or additives for high thermal performance
coatings. The flexible blankets are obtained by adding fibres in the gel before the
drying process (Cabot Corporation, Boston, MA, USA; Aspen Aerogels Inc.,
Northborough, MA, USA); the thermal conductivity is about 0.013 W/m K, but
the cost is about 10 times higher than a conventional material with similar
performance (Aspen aerogels 2012);
2. transparent aerogels, such as monolithic aerogels for superinsulating windows.
Twenty years ago, several glazing prototypes with monolithic aerogel were
involved in a project (HILIT project, in Schultz and Jensen
2008
), but at the
moment, no commercial products are available because of the synthesis process
is very time and cost demanding;
3. translucent granular silica aerogels (often called nanogel), used to realize highly
energy-efficient windows and skylights. Different daylighting systems in
PMMA are now commercialized: depending on the gas filling and the external
and internal panes and properties of granular aerogel in the interpace, U-values
can be lower than 0.3 W/m
2
K.
Fig. 2 Aerogel insulation material for building applications: opaque blankets (a), monoliths (b),
and granular aerogels (c)