Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
5.2 Internal-Melt Ice Thermal Storage
The basic difference between an internal melt and an external melt systems is that
glycol (or brine) solution is used for charging and discharging of storage tank,
which is not the case for an external ice melt concept (EVAPCO Inc.
2007
and
Yau and Rismanchi
2012
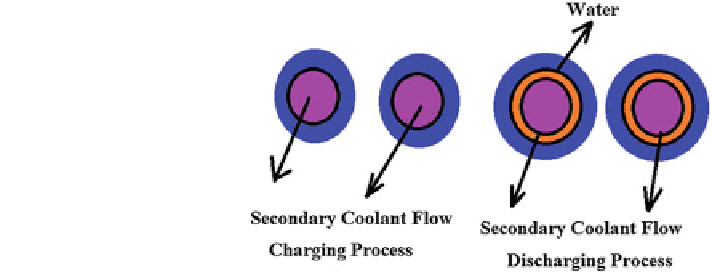
). The schematic representations of the charging and
discharging processes in an internal melt ice TES is shown in Fig.
14
.
Typically, during the charging process (at off-peak conditions), the cooled
glycol from chiller while flowing in the primary circuit transfers the cold energy to
the surrounding water filled inside the tank. This in turn enables the water in the
tank to freeze into ice, which builds up to the predetermined quantity. On the other
hand, during the discharging process (on-peak conditions), the warm glycol
solution entering from the building side (secondary loop) transfers the heat energy
to the chilled water (or ice).
By this, the built-in ice gets melted, and subsequently, the glycol solution is
cooled to the required temperature. Here, the chilled water present in the storage
tank remains static, and the heat transfer mechanism involved in ice storage
processes are largely due to the flow of glycol through the primary cooling coil
loop. The merits of internal ice melt system include the following:
• the benefits of having a closed-loop arrangement,
• effective control of glycol solution temperatures in both primary and secondary
sides,
• COP of primary chiller plant is better than that experienced with an external
melt system,
• energy redistribution in buildings is possible with time-dependent charging and
discharging modes of operation, and
• water in the storage tank only changes its phase in the due course of operation,
which helps to reduce the pumping energy consumption.
Limitations of the ice storage systems include the following:
• thermal losses occur during energy storage and energy redistribution processes,
Fig. 14 Charging and
discharging procedure of an
internal ice-on-coil storage
system