Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
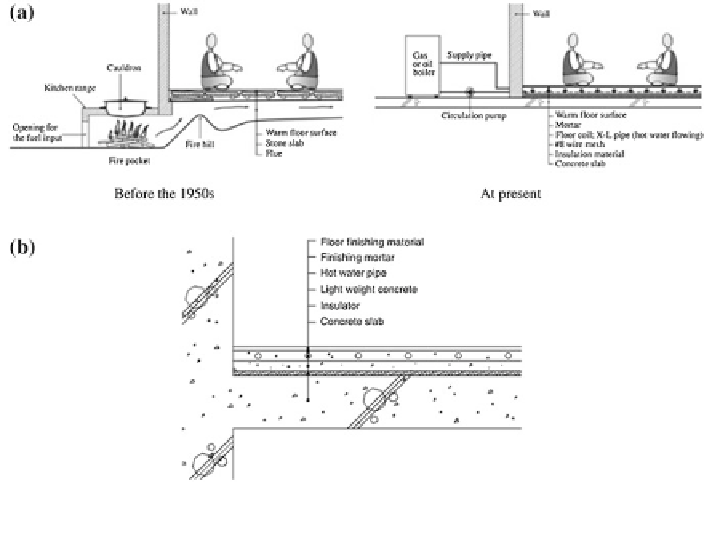
Fig. 3 a The radiant floor heating system and b standard floor formation for the Korean Ministry
of Land (Jeon et al.
2013
)
through natural convection effects. The schematic representation of the radiant
floor heating system and the standard floor formation (Jeon et al.
2013
) are shown
in Fig.
3
a-b.
It should be noted that for the buildings that are located in moderate to cold
regions and equipped with this system, the floor surface temperature has to be
maintained above 15-17 C, which will prevent from any condensation of room
air onto the floor surface. On the other hand, the same system can be tuned for
providing heat energy storage to the building floor structure during winter seasons.
By supplying the hot water (either derived from waste heat source or water
heating) through the embedded underfloor pipe lines, the slab structure is heated,
and the energy is then stored sensibly.
The rate of energy stored in the slab component depends mainly on the thermal
conductivity, diffusivity, specific heat capacity and thickness of the ingredient
building materials. The merits of the underfloor slab storage system include the
effective redistribution of thermal energy into conditioned spaces, increased heat
transfer rate between floor surface and indoor air through radiation, reduced
condensation risks and lower operating costs. Providing proper control mechanism
would help to adjust the set-point temperature fluctuations as well as the flow rate
of heat transfer fluid throughout the operation of the storage system in buildings.