Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
In building industry, the uses and purposes of fibrous insulation products are
mainly for cavity walls, solid walls, structural insulated panels, roof insulation, and
insulation materials for heating systems as well as water services. Each product
has its own role in different applications depending on its general properties. All
products are likely to have both advantages and disadvantages for use in certain
applications. Therefore, every property required for an application influences
material selection in varying degrees. When choosing a material, consideration
needs to be given such as to the thickness requirement, fire resistance, acoustic
performance, breathability and reliability (BNIM01 2008). Very often, a combi-
nation of different types of product would help to satisfy a wider range of
requirements. Nevertheless, the very first step is to select raw materials. The
selection rules are the same as those applied to the products, according to many
criteria including their thermal, physical, mechanical and chemical properties,
cost, and their human and environmental safety. Obviously, the basic criteria are
the resources of the particular type of raw material, the cost and the manufacturing
progress.
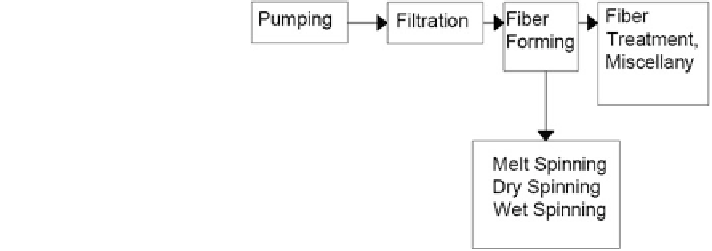
Fundamentals of fibre manufacturing process comprehensively cover the prin-
ciples of transport phenomena and chemical reaction engineering (Weinberger
1996
). Figure
9
summarizes the four main areas of fibre manufacture: pumping,
filtration, fibre forming and fibre treatment, focusing on the fundamentals asso-
ciated with the transport phenomena of fibre production based on the study of
(Weinberger
1996
).
For vegetable fibres, the most commonly used manufacturing process can be
roughly divided into three different steps involving harvesting, fibre processing
and utilization (Dam
1999
), depending on many different factors, such as quality
of the raw materials and quantity of the final product. Figure
10
presents the steps.
Harvest is the process of collecting mature vegetables from the fields which,
basically, involves two processes associated with vegetable fibre: pulling and
reaping. The raw material, flax and hemp for example, is pulled using specific
machines or hands. After pulling, the plants are laid on the filed for drying before
going through retting and extraction process.
The extraction and retting process has a major impact on the fibre product
quality. Vegetable fibres can be extracted manually or mechanically by machines
Fig. 9
Synthetic fibre
module