Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
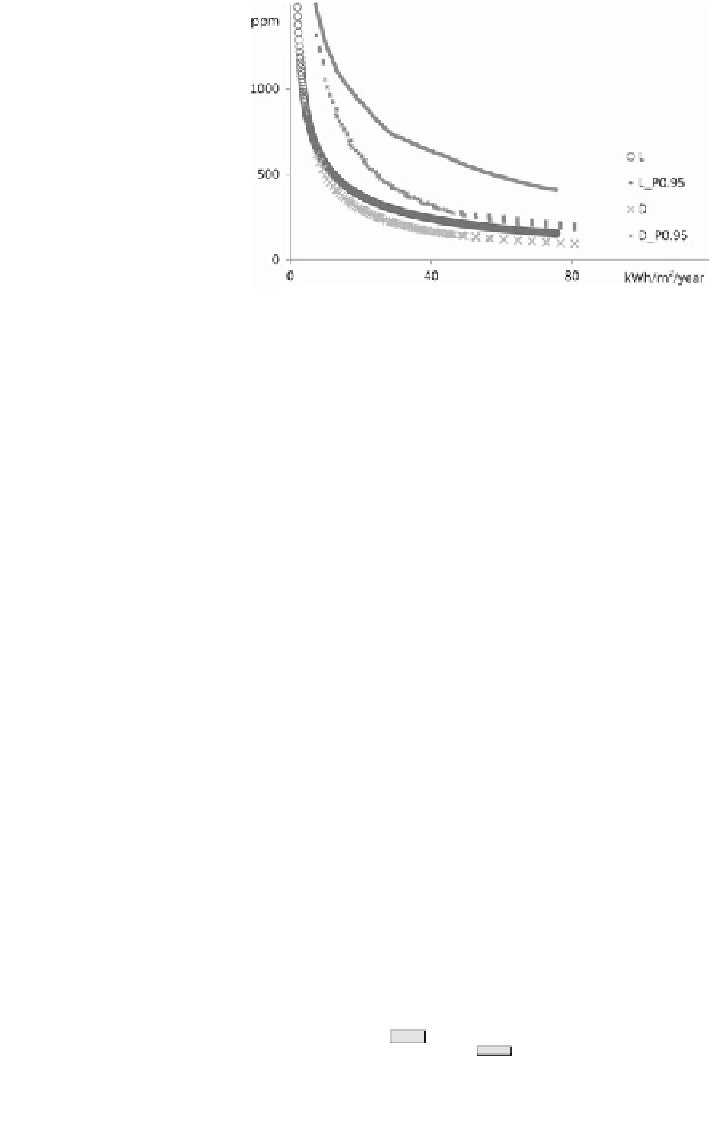
Fig. 3 Pareto optimal mean
exposure (ppm) versus
ventilation heat loss (kWh/
m
2
/year) in a Belgian
detached house for
mechanical ventilation
(D) and ventilation by
leakage
Since the available driving forces are variable and leakage is usually concen-
trated around details in the building envelope (Van Den Bossche et al.
2012
;
Relander et al.
2012
), the distribution of the fresh air in the dwelling is not nec-
essary correlated with the needs. This reduces the overall efficiency of air leakage as
a ventilation strategy, especially when compared to mechanical ventilation. This is
dioxide trade-off in a detached dwelling in Belgium is shown for a mechanical
ventilation system and for ventilation through leakage. The performance of the
former is systematically better. Although the difference is smaller, the same is
found when the optimal performance of ventilation by leakage is compared to that
of natural ventilation.
Due to the intensification of energy performance requirements for new build-
ings, the building industry is moving into more tight construction, favouring more
efficient types of ventilation (Chen et al.
2012
). This is typically achieved by
reducing the number of joints in the construction (Pan); 10 ACH at 50 Pa is a
typical value for older construction (Sinnott and Dyer
2012
; Bossaer et al.
1998
)
and mild climates (Sfakianaki et al.
2008
; Montoya et al.
2011
), but high-per-
formance buildings are up to 10 times more airtight. This is clearly visible in time
evolution of air tightness in Belgium shown in Fig.
4
in ''
Toxicity issues: Radon
'
' .
Fig. 4 Evolution of leakage
rates (n
50
) for single family
houses in Belgium. Boxplots
for social housing from the
1960s ('case-study'),
standard construction from
the early 1990s and after
2000 ('Senvivv' and
'UGent'), frontrunners
('BD') and low-energy
houses ('BD LEH')
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
case-study
60
n=24
Senvivv
80- 90
n=51
UGent
~2005- 10
n=51
BD
~2005- 10
BD LEH
~2005-
n=78
10
n=55