Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
from other factors influencing the building energy consumption, a technique based
on cluster analysis proposed in (Yu et al.
2011
) is used.
An occupant behavioural model based on HMMs is proposed by Virote and
Neves-Silva (
2010
). The objective was to capture the user dynamics and model the
user actions in a building regarding the interaction with the lighting system. In this
chapter, these models are improved and extended to the simulation process. The
novelty of this model is that it behaves as a generator and not as a behaviour
recognition model. That is, the model does not intend to explain, infer or recognise
the occupant behaviour based on external constraints. In its place, it generates a
similar occupancy behaviour pattern as the occupant generates.
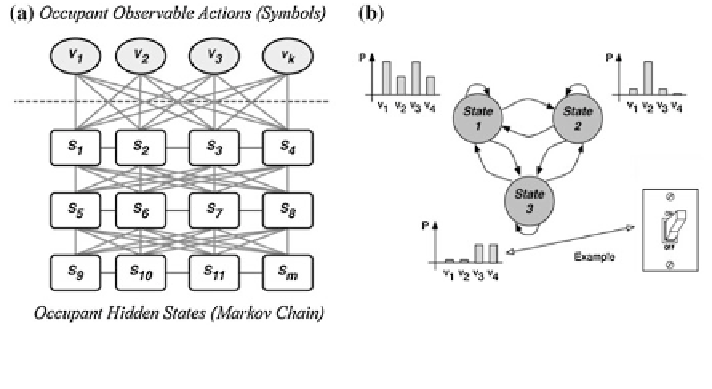
3 Proposed Methodology
3.1 Stochastic Occupant Behavioural Model
The objective of developing a behavioural model for the building occupant, rep-
resented in Fig.
3
is to be able to predict the impact of the occupants' decisions in
the overall energy consumption. Taking a simple example in lighting, how often
will the occupants switch off the lights when exiting a single office room and what
is the impact on energy consumption? The model reflects the behaviour of an
aggregate population expressed by the probability of performing an action.
Of course, occupants' actions are the result of a complex behaviour charac-
teristics related with education, environmental awareness, involvement with the
economic impact, among other factors. Thus, it is possible to characterise occupant
behaviour as a composition of observable states representing actions; and hidden
Fig. 3 a Generic structure of a Hidden Markov Model and b concretization of the generic hidden
Markov model with example of emission symbols