Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
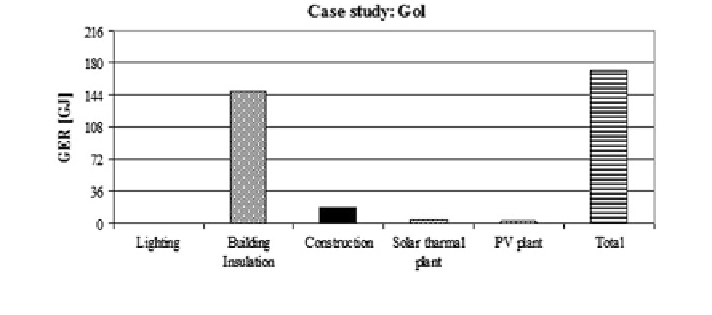
Fig. 4
Contribution of each retrofit actions to the GER in Gol case study (Hol Church)
3.2.2 Case Study: Gol
The retrofit of Hol Church (Gol) included the following actions:
• refurbishment of the building roof and the ground floor, by means of new
thermal insulation and high-efficiency windows to reduce the thermal losses and
the lighting need,
• installation of PV panels and of a solar thermal system,
• introduction of efficient lighting.
Figure
3
compares GER to total energy saving, and Fig.
4
shows a contribution
to GER of each retrofit action. It is observed that the highest GER is due to the
building insulation, while the lighting system contribution is negligible.
The refurbishment of the building envelope is also the retrofit action that involves
the highest energy saving (8,612 GJ).
The refurbishment of the building roof and floor provides a yearly saving of
primary energy of 246 GJ/y (443 MJ/(m
2
y) for a total floor area of 555 m
2
). The
installation of the PV panels provided a yearly saving of 1 GJ/y of electricity. The
related primary energy saving is 1.5 GJ/y (3 MJ/(m
2
y)). The solar thermal system
involved a primary energy saving of about 9 GJ/y (16.2 MJ/(m
2
y)). Concerning
the introduction of efficient lighting, the yearly saved electricity was 35 GJ/y and
the related primary energy saving was 50 GJ/y, with a primary energy saving per
unit of floor area of 90 MJ/(m
2
y).
3.2.3 Case Study: Plymouth
The retrofit of Plymouth College included the installation of two 6-kW wind
turbines to reduce the electricity demand of the site.
The yearly saving of electricity provided by the retrofit action is 41.4 GJ/y with
a primary energy saving of 143 GJ/y. The total floor area is 5,794 m
2
, and the
specific primary energy saving is 24.6 MJ/(m
2
y).No intervention for heat saving
was performed.