Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
(CP4 EPSPS) (Hern
´
ndez et al.
2003
). PCR was performed three times per aliquot,
and samples with positive results at least twice were judged as positive (Chowdhury
et al.
2003
). The identity of amplification was verified by the ABI PRISM
®
310
Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems) and confirmed by comparison with all
sequences in the international nucleotide nonredundant databank.
33.3 Results
The quantity and purity of DNA extracted from fresh samples were higher than
samples stored at
20
C (ng/
l: 51.6 vs. 20.8; A
260
/A
280
: 1.7 vs. 1.4). The
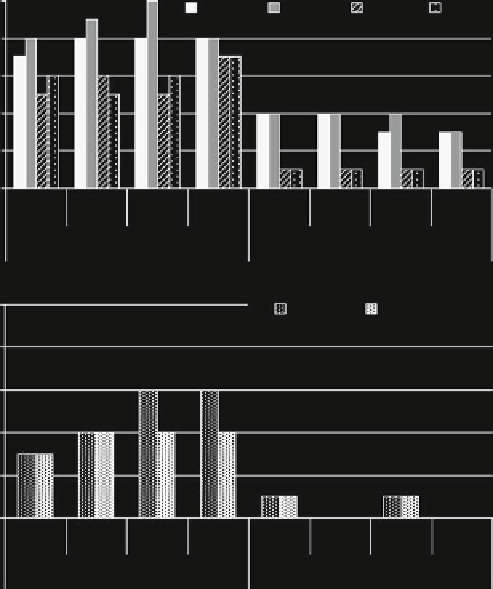
frequency of the chloroplast sequence, for both groups, ranged between 70 and
100% in fresh samples and between 30 and 40% in stored samples (Fig.
33.1a
).
In the samples positive for the chloroplast sequence for both groups, the fragments
of specific soybean gene were detected (56-88% in fresh and 25-33% in stored
m
a
10
Clor_A
Clor_B
Lec_A
Lec_B
8
6
4
2
0
1°
2°
3°
4°
1°
2°
3°
4°
fresh DNA extracted
DNA stored at -20°C
b
10
35s
CP4 EPSPS
8
6
4
2
0
1°
2°
3°
4°
1°
2°
3°
4°
fresh DNA extracted
DNA stored at -20°C
Fig. 33.1 Detection of chloroplast gene (clor, a), soybean lectin gene (lec, a), 35S promoter (35S, b),
and CP4 EPSPS gene (CP4, b) fragments in milk samples from goats fed conventional (a)or
transgenic (b) soybean s.e. meal