Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
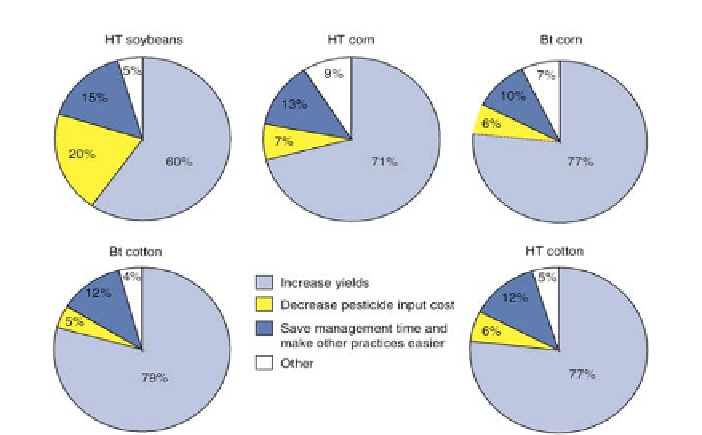
Bt crops have insect resistant traits; HT crops have herbicide tolerance traits.
Sources: USDA Economic Research Service using data from Agricultural Resource
Management Survey (ARMS) Phase II surveys: 2010 for corn, 2007 for cotton,
and 2006 for soybeans.
Figure 7. Farmers' reasons for adopting genetically engineered crops.
Farm-Level Economic Impacts of GE Crop Adoption
The impacts of GE crop adoption vary by crop and technology. Many
studies have assessed the factors that influence adoption as well as the impacts
of GE crops on yields, net returns, and pesticide use (table 4; Fernandez-
Cornejo and McBride, 2002). Over the first 15 years of commercial use, GE
seeds have not been shown to increase yield potentials of the varieties.
13
In
fact, the yields of herbicide-tolerant or insect-resistant seeds may be
occasionally lower than the yields of conventional varieties if the varieties
used to carry the HT or Bt genes are not the highest yielding cultivars, as in
the earlier years of adoption (Fernandez-Cornejo and Caswell, 2006; National
Research Council, 2010).
14
However, by protecting the plant from certain
pests, GE crops can prevent yield losses to pests, allowing the plant to
approach its yield potential.