Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
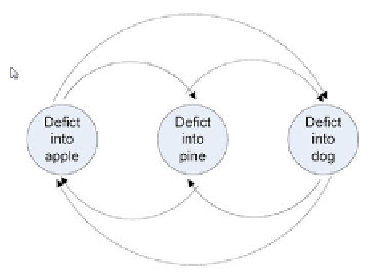
Fig. 1. Conditional dependencies between semantic categories. Graph with cycles.
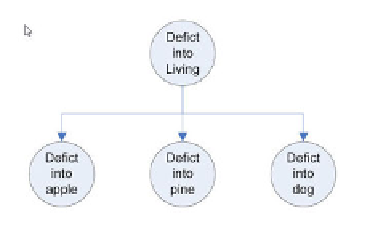
Fig. 2. Conditional dependencies between semantic categories. Graph without cycles.
The fig.3 represents the qualitative modelling of the Bayesian Network.
The Construction of the qualitative model is one of the most complex tasks
in the modelling of the Bayesian Network. In order to be able to generate
the quantitative model automatically, it is necessary to have a large num-
ber of representative cases of the population. In many instances it is neces-
sary to have epidemiological studies, and this task is not trivial at all. There
are epidemiological studies that provide the distributions of combined prob-
abilities thus: P(DEMENTIA, SEX), P(DEMENTIA, AGE), P(DEMENTIA,
EDUCATIONAL LEVEL), P(ALZHEIMER, SEX), P(ALZHEIMER, AGE),
P(ALZHEIMER, EDUCATIONAL LEVEL). In this instance it is very useful
to use the Naive Bayes simplifier to calculate the conditional probability ta-
bles. The Naive Bayesian Method or Naive Bayes starts from the assumption
that the diagnosis is exclusive (there cannot be two diagnoses at the same time)
and exhaustive (there are no other diagnoses possible). In our model two condi-
tions are fulfilled because we only aim to diagnose cognitive deterioration com-
patible with Alzheimer at three levels or degrees. With these premises we can
use the Naive Bayes simplifier and it is therefore possible to calculate all the
conditional probabilities that we need for the model, as can be shown below:
P(Alzheimer | sex, age, educational level) =
α
* P(Alzheimer)*P(sex |
Alzheimer) * P(age|Alzheimer)* P(Educational Level| Alzheimer)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search