Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
1
1
0.8
0.8
0.6
0.6
P
P
0.4
0.4
0.2
0.2
0
0
8
16
24
32
40
48
56
64
72
8
16
24
32
40
48
56
64
72
trial
trial
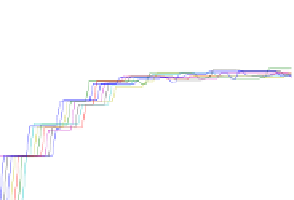
Fig. 3.
Learning process of the Markov model: deterministic order (left) and random
order (right). The parameters were
p
suc
=
p
sr
=
p
or
=0
.
9. Every line shows the
probability of success
P
(cf. 5) for the concerning object.
which results in ten trials on every object and 80 trials in total. Further we
distinguish a deterministic and a random order. In case of a deterministic order
the objects are presented in the same succession in every cycle. For the random
case the succession of the objects is randomised in every cycle.
3 Analysis of the Markov Model
The advantage of a Markov model is the possibility to an analytic view on the
learning process. The following analysis is limited on the explicit associative
learning task (Fig. 1) on a
single
object. This is the model as it is described
above until (4). The steady state and convergence of the Markov chain illustrate
the correlation of the parameters
p
suc
,
p
sr
and their influence during learning.
We gain no further finding on the role of the parameter
p
or
by this analysis,
since this parameter is influential on the learning process for a
series
of objects.
The steady state
has its relevance in the asymptotic character of the state prob-
ability vector
π
(
t
)for
t →∞
. For convenience, we shorten
T
in (4).
Repetitive replacement in (4) of
π
(
t
+1) by
A
·
π
(
t
) gives the steady state:
T
·
C
=
A
t
π
stat
= lim
t→∞
A
π
(0)
=
π
stat
=
A
π
stat
,
(7)
leading to the linear system of equations
π
j
stat
=
i
A
ij
π
i
stat
,
, j
∈
S.
(8)
With the analytic solution for the steady state (8), we are able to calculate the
final state probability vector of the Markov chain. A closed solution can be found
with a computer algebra system. The final probability of success
π
16
stat
depends
only on
p
suc
and
p
sr
in a fraction which numerator is a sixth-degree polynomial
of
p
sr
and second-degree of
p
suc
. The denominator is a fourth-degree polynomial









































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search