Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
(12)
(13)
is the dimension of the antenna element,
H
(1
,
2)
l
krh
(1
,
2)
l
Where
L
(
k, r
)=
(
k, r
)
and
h
(1
,
2)
l
(
k, r
)
[14, ch.6-1] is the spherical Hankel function of the first and second
kind and
H
l
is the derivative w.r.t
r
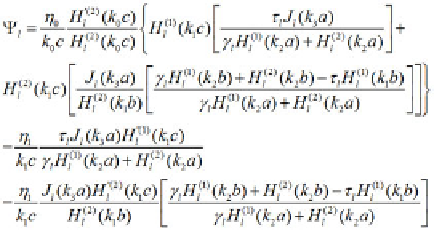
. The coecients presented in (12) and (13)
are simply the result from solving the BVP.
2.2 Beamforming Technique
After obtaining the received current signal equation in the previous section it is
now possible to consider the beamforming technique that will allow the array to
eciently scan the environment. By proper scanning the array will determine
the source from which the source H-field originated.
The idea behind the technique is based on the orthogonality principle of the
TE modes. To begin the analysis the received input current at the ith antenna
element is expressed as follows.
(14)
Where
I
i
is given by (11) and
n
i
is a zero mean white Gaussian noise. Each
signal
I
i
will be multiplied by a weight factor (i.e. magnitude and phase)
g
i
and
then all the signals from all the elements are added up to produce one output
current
I
out
given by equation (15).
(15)
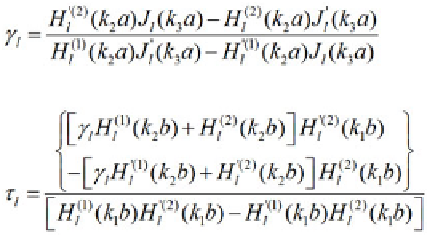


Search WWH ::

Custom Search