Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
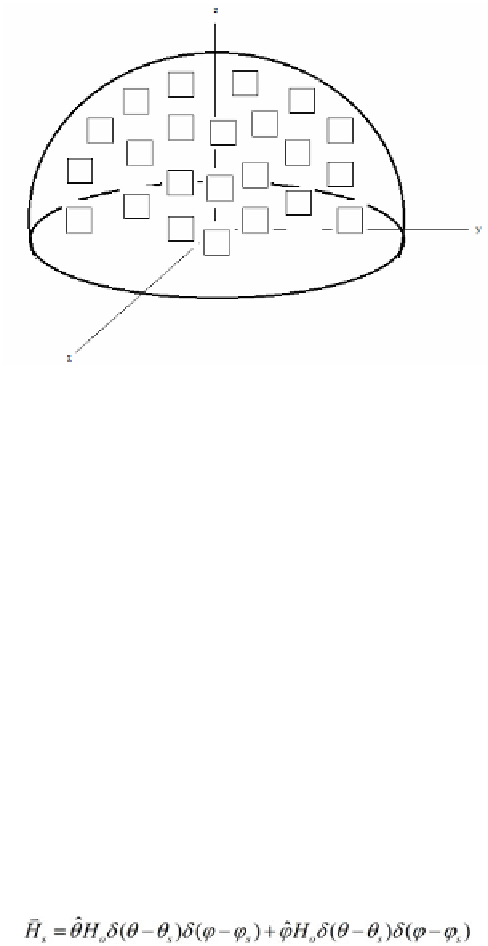
Fig. 2.
Loop Antennas Placed on the Human head
space), region (1) is the skin, region (2) is the skull and finally region (3) is the
brain. The 42 antennas are going to be placed on top of the skin surface and
they will cover a hemispherical surface of radius
(Fig. 2).
Since the human head is approximated to be spherical, it is therefore obvi-
ous that the boundary value problem will be solved by utilizing the spherical
coordinate system. According to [14, ch.6-1], any electromagnetic problem with
spherical symmetry can be solved using the electric vector potential
F
r
and the
magnetic vector potential
A
r
in spherical coordinates. Any electromagnetic wave
can be decomposed into two orthogonal sets of functions which are the
c
trans-
verse electric (TE)
A
r
waves. Both vector
potentials are solutions to the Helmholtz equation [14, ch.6-1] and can be used
to find the fields in all four region. In the paper the fields will be expressed in
terms of the TE modes only since the TM modes are smaller in comparison. The
problem starts with the assumption that there is a localized (i.e. assumed as a
delta function) radiating magnetic field in region (3) at a distance
r
s
F
r
and the
transverse magnetic (TM)
coming
from the direction
denotes source). Since the H-field is
localized it can be described by the following equation which.
(
θ
s
,
ϕ
s
)
(the subscript
s
(1)
Where
H
o
represents the magnitude of the H-field. To solve the BVP equation
(1) must be expanded in terms of the TE modes as shown in (2):
(2)
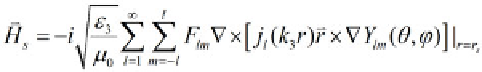
Search WWH ::

Custom Search