Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
center. Successive split points can be set, while selected sector aperture is wide
enough, allowing robot to pass across narrow passages and to drive in crowded
environments. For goal reaching a virtual split point can used to select a sector
in goal direction.
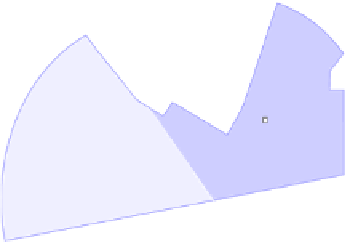
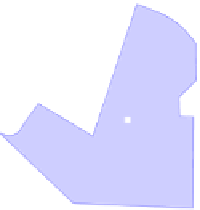
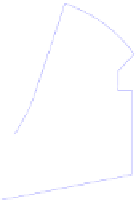
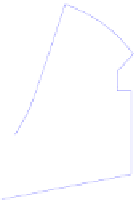
Fig. 4.
Bad split point selection example case. In a) the center of area for the full free
area becomes inaccessible in the point marked with an arrow and it becomes the split
point. Due to goal direction right sector is selected and robot follows the new area
center marked with AC b). But area center path is not enough far away from obstacle
leading robot to a crash in c). It would be better to set the split point at the nearest
corner of the obstacle as in d), so area center path is far away enough from obstacle.
The selected sector has dark blue color and the unselected one has a lighter color.
Correct split points localization is very important for a safe navigation. Using
raw range measures the basic method usually provides a safe navigation, but
there exists some situations, specially when doing goal tracking, where the po-
sition of the split point is not adequate yielding a dangerous situation. Sample
situations depicted in figs 4 and 5 are taken from experiments described in [13].
The problem arise from selecting a sector, after split, with highly protruding
corners. Selecting as split point the nearest segment end of those segments with
some end between the area center and the bisector of original sector plus an off-
set, we can get sectors with less noticeable protuberances near the robot path,
see fig. 4 d).






























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search