Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Thus, if
Σ
is the set of proposed routes by agents, the route
a
is declared
winner in an auction if and only if one of the following equations is satisfied:
∃
aΣ,
∀
bΣ, a
=
b
∧
(
a
∩
b
)=
φ
(1)
∃
aΣ,
∀
bΣ, card
(
a
−
C
a
)
≥
card
(
b
−
C
b
)
(2)
where
C
a
=
∪
cΣ, c
=
a
(3)
C
b
=
∪
cΣ, c
=
b
(4)
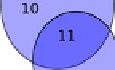
Fig. 1 shows an example of route selection in terms of set theory. Each proposed
route is denoted with a letter (
A, B, C,
...), each route is composed by stretchs
denoted with numbers (
1,2,3,
...). In the situation showed in this figure, routes
A
and
E
will be winners and agents that proposed routes
B, C
and
D
will have
to propose a new routes and start a new auction process.
Fig. 1.
Route selection process
Agent.
The aim of the agents is to achieve that all the edges of the graph will
be visited. To accomplish this objective, all members of the team negotiate the
routes that best fit to reduce the number of times an edge is inspected.
Throughout the execution of its algorithm (described in Fig. 2), the agent
checks if it has a precalculated route. If the route does not exists, then it will
calculate the best fit route to its current position. This route selection process
is described later.
If a route exists, then the agent checks if this route is confirmed. We employ
the term
to call the routes which have been won by the agents
in a previous negotiation with other teammates. Normally, these routes can be
executed by the robots without the need of communicate with the central server.
If the route is not confirmed and communication with central server is possible,
then an auction process will start. In this auction all routes presented compete.
If an agent wins an auction, its route is confirmed and it can execute it. Agents
confirmed route












Search WWH ::

Custom Search