Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
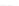
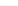
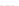
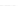
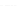
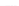
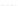
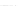
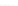
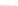
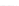
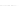
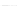
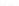
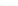
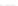
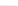
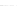
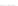
Fig. 2.
Effects of coupling betweeen pyramidal neurons and FS interneurons on the
networks dynamics. Left panel:
g
PF
=0
.
3
mS/cm
2
,
g
FP
= 0. Middle panel:
g
PF
=0,
g
FP
=1
mS/cm
2
. Right panel:
g
PF
=0
.
3
mS/cm
2
,
g
FP
=1
mS/cm
2
. For all panels it
is:
g
e
=0
.
5,
g
i
=0
.
25,
g
el
=0,
I
P
=3
.
5
μA/cm
2
,
I
F
=1
.
3
μA/cm
2
,
N
PY
= 80,
N
FS
=
20. For all panels the gray vertical bars represent the firing times of the pyramidal
cells, while the black ones those of the FS interneurons.
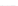
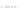
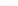
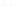
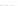
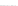
Fig. 3.
Effects on the neural networks dynamics arising from the change of the reversal
potential value of the inhibitory synapses. For all panels it is:
g
e
=0
.
5,
g
i
=0
.
25,
g
PF
=0
.
3
mS/cm
2
,
g
FP
=1
mS/cm
2
,
I
P
=3
.
5
μA/cm
2
,
I
F
=1
.
3
μA/cm
2
,
N
PY
= 80,
N
FS
= 20. Left panel:
V
FP
=
V
FF
=
−
50,
g
el
= 0. Middle panel:
V
FP
=
V
FF
=
−
50,
g
el
=0
.
1. Right panel:
V
FP
=
V
FF
=
−
45,
g
el
=0.
In the left panel of figure 3 the results obtained in the case
V
FP
=
V
FF
=
50
mV
are shown. The comparison with the results corresponding to
V
FP
=
V
FF
=
−
80 (see right panel of figure 2) shows that the prominent effect is
a strong increase of the firing activity of both networks. The activity of each
network is characterized by bursting and that occurring in the population of
coupled FS cells is caused by the presence of excitatory synapses from pyramidal
−






















































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































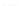












































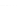






































































































































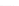




































































































































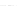













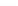




















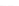































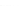

































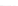


























































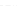




























































































































































































































































































































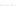



















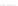













































Search WWH ::

Custom Search