Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 7-23
Oldest vegetated roof (1650), northern Sweden, seventeenth century.
we often find that someone in the distant past had the same idea, although for a
somewhat different purpose (Figure 7-23).
Design and Function
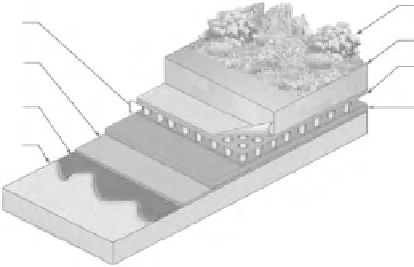
Extensive vegetated roof covers (Figure 7-24) are 6 in. or less in depth and are
typically intended to achieve a specific environmental benefit, such as rainfall
runoff mitigation, or to help reduce building energy needs for cooling. Although
some installations are open to public access, most extensive vegetated roof covers
offer at most visual access for the public. To make vegetated roofs practical for
installation on conventional roof structures, lightweight materials are used in the
preparation of most engineered media. Developments in the last 40 years that have
made these systems usable include (1) recognition of the value of vegetated covers
in restoring nearly open-space hydrologic performance on impervious surfaces,
(2) advances in waterproofing materials and methods, and (3) recognition of the
multiple environmental benefits provided by vegetated roofs.
Vegetation
Aeration,water storage,
root barrier
Membrane protection
and root barrier
Roofing membrane
Growing medium
Drainage, and
filter layer
Insulation
Structural support
Figure 7-24
Vegetated roof system: extensive.











Search WWH ::

Custom Search