Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
71
overs are rare events, we only need to consider two cross-overs as shown in
Fig. 3-3.
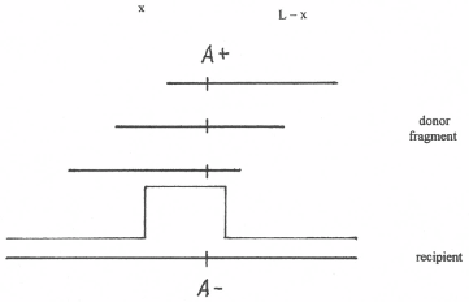
Figure 3-3.
The basic mechanism of obtaining an A+ transductant.
Cross-overs are proportional to the length of the involved DNA segment,
and the constant of proportionality can be denoted by µ. Since we have no
idea of the distance from the left end of the donor DNA fragment to the
marker A+, we shall designate it as x. However, we know that the entire
length of the donor DNA fragment is fixed and can be denoted by L. Thus,
the distance from the marker A+ to the right end of the donor DNA
fragment is L-x. In random generalized transduction, a uniform distribution
of various pieces of donor DNA fragments is assumed and the distribution
constant is denoted by c. Then, the chance of obtaining an A+ transductant
can be calculated by integrating over all relevant values of x, i.e. from 0 to
L: