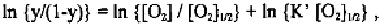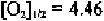Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
In order to calculate percentage saturation, y, at a certain oxygen pressure
we need to divide the total number of oxygen molecules associated
with hemoglobin by the total number of available sites for oxygen
molecules:
A factor of 4 can be cancelled from the numerator and the denominator,
giving the equation in Pauling's original paper. He used p to denote
To compare his theoretical model with the experimental data of Roughton
et
al.
in the Hill's plot, we can estimate the asymptotic expressions of y/(1-y)
for very low and very high oxygen pressures. Since
we have, for very low oxygen pressure, the following:
which is a straight line of slope one in the Hill's plot. Since
mm Hg, K' can thus be determined from the experimental data of Roughton
et al.
Similarly, for very high oxygen pressure, we have:
which is also a straight line of slope one in the Hill's plot. The value of
can also be determined experimentally. Indeed, very few experimental
measurements of hemoglobin saturation other than those of Roughton
et al.
were accurate enough to exhibit these important features in the Hill's plot.