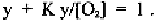Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
42
The equilibrium constant K can be determined by drawing a horizontal line
at y = 0.5 or 50%, intersecting the curve, and dropping a vertical line to the
[O
2
] axis. It is equal to the oxygen pressure at half saturation, or [O
2
]
1/2
.
Also, the initial slope of the curve is equal to 1/K. This same equation will
be encountered again in Chapter 4 for simple enzyme kinetics.
Thus, the binding of oxygen by myoglobin is simple. However, biochemists
do not like to deal with curves. Two other graphs or straight lines are
commonly used. One plots 1/y as a function of 1/[O
2
] as shown in Fig. 2-4.
In this case,
The straight-line extrapolation of the experimental data points insects the
horizontal axis at -1/K.
Fig. 2-4.
Plot of 1/y against 1/[O
2
].
The other plots y against y/[O
2
] (Fig. 2-6) or vice versa. Here,