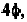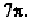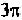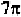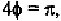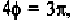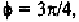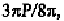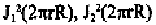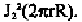Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
207
The arrows representing the amplitudes on the first four layer lines are
scaled to the maximum values of J
1
(x), J
2
(x), J
3
(x) and J
4
(x) as listed in Table
8-1.
The absence of any intensity spot on the fourth layer line (Figs. 8-1 and 8-5)
suggests that the vectors representing the amplitudes of the two helices must
be opposite to each other in the phase plane. Thus, the phase difference on
the fourth layer line, is equal to or However, the situation
for is similar to that of (Fig. 8-5), and to (Fig. 8-4). For
or the addition of the two amplitudes on the first layer line (Fig. 8-
6) results in a large vector. Thus, the intensities of the spots on the first four
layer lines would be very strong, strong, weak and absent, quite different
from those observed for DNA fibers (Figs. 8-1 and 8-5). On the other hand,
for or the resultant amplitude on the first layer line is
much smaller than individual amplitude (Fig. 8-7). Intensities would then
be weak, strong, strong and absent on the first four layer lines, as observed
experimentally (Figs. 8-1 and 8-5).
Therefore, the relative displacement between the two helices will be
or 3P/8, as shown in the original sketch by Watson and Crick (1953).
Since the intensities predicted by the above double helix on the first, second
and third layer lines must locate at values of correspond to the first
peaks of and or roughly at 1.86, 3.05 and 4.20
respectively, and since the spot on the equatorial layer line corresponds to a
value of equal to about 3.14, we can conclude that the Watson and
Crick double helical DNA secondary structure is in agreement with the X-
ray diffraction picture of the lithium salt of DNA at 66% relative humidity
(Fig. 8-3). In that picture, the intensity spot on the second layer line is
located directly above that on the equatorial layer line, suggesting that the
intensity on the second layer line indeed corresponds to
BIOLOGICAL CONSEQUENCES OF DNA DOUBLE HELIX
Indeed, the DNA double helical structure has been considered as the most
fundamental aspect of modern day molecular biology. It consists of two