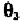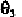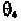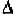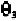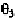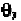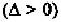Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
185
In Fig. 7-7, the C
5
' atom is placed at the origin, and the C
5
'-O bond along
the negative z-axis. The P atom is in the x,z-plane. The angle is the
angle between the x,z-plane and the plane formed by the C
4
'-C
5
' bond and
the C
5
'-O bond. In Fig. 7-8, the P atom is placed at the origin, and the P-O
bond on the 5'-end along the negative z-axis with the C
5
' atom in the x,z-
plane. The angle is the angle between the x,z-plane and the plane defined
by the (C
3
'-)O-P and the P-O(-C
5
') bonds. In both cases, the positive
and angle follow the right-hand rule along the z-axis. Due to the
relatively large van der Waal radius of the P atom, the tolerance is
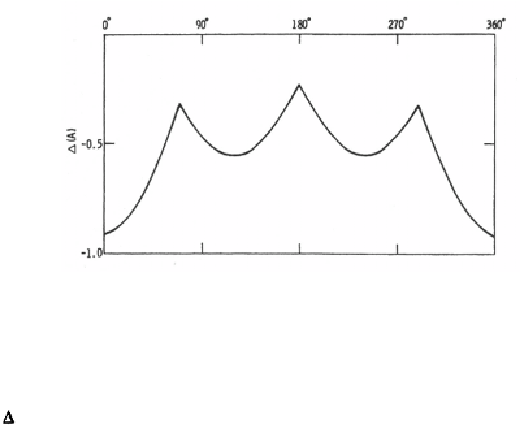
calculated for various values of for the P atom only and illustrated in Fig.
7-9. As expected, when the P atom is opposite to the two H atoms on C
5
',
i.e.
there is least steric hindrance.
Other locations for low
tolerance are around
of 110
0
and 290
0
.
Figure 7-9.
Tolerance as a function of
for P atom only.
Since the variation of from 180
0
to 360
0
is similar to that from 180
0
to 0
0
,
only the latter range is considered together with the for tolerance
calculation involving other atoms. The result is shown in Fig. 7-10, with
the P atom excluded. The region with tolerance greater than zero
is
stippled.