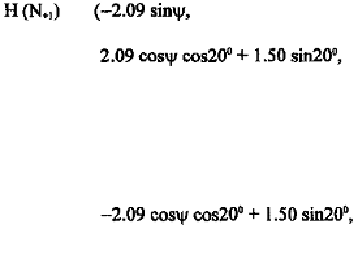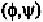Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
139
(OLD)
(NEW)
Since the minimum allowable distances between non-bounded atoms are
usually accurate only to the first decimal place (table 5-4), some error in the
second decimal place of the above coordinates can be tolerated. In general,
such hard-sphere approximations give reasonable good result.
OTHER INTERACTION POTENTIALS BETWEEN NON-
BOUNDED ATOMS
The interaction between non-bounded atoms can be calculated theoretically
by dipole-dipole interactions (Schiff, 1955) for relatively large separations.
This gives an attraction between non-bounded atoms proportional to the six
power of their separation For interactions within short distances, various
empirical potentials have been suggested. One of the most commonly used
potentials to study protein folding is the Lennard-Jones potential (see, for
example, Fogolari
et al.
, 1996; dementi et
al.
, 1999). In this case, there is a
repulsion between non-bounded atoms proportional to the twelve power of
their separation. Sometimes, the Buckingham potential (see, for example,
White, 1997) is also used. The repulsion is considered to be exponential.
Allowed regions in the plot (Brant
et al.,
1967) can also be calculated
using these potentials (Fig. 5-15, 5-16). They are in general somewhat
different from those estimated with minimum contact distances as discussed
by Ramakrishnan and Ramachandran (1965). However, whether they give
better results than hard-sphere approximations remains to be seen.