Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
2.4. Ping-Pong Algorithm
High-throughput technologies are now used to generate different
types of data from the same biological samples. A central challenge lies
in the proper integration of such data. To this end, we proposed the
concept of comodules, describing coherent patterns across paired
datasets, and conceived several modular methods for their identifica-
tion. We proposed the ping-pong algorithm (PPA; see Fig. 6) and
other modular schemes for the identification of such comodules.
56
For
example, we studied the integration of gene expression and drug
response data from the NCI60 project. For this study, 60 tumor cell
lines were analyzed using both microarrays
57-59
and assays monitoring
their growth when subjected to a large number of chemical com-
pounds.
60,61
Thus, each cell line is described by two profiles, one for
the expression of each gene and one for its resistance to each drug.
3
1
R
E
D
G
C
4
2
M
GCD
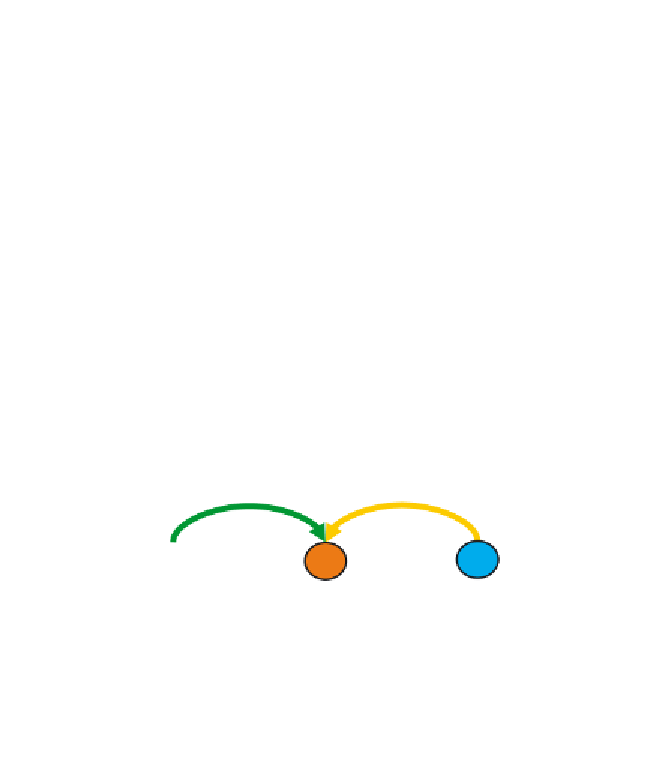
Fig. 6.
The ping-pong algorithm starts with a candidate set of genes
G
and uses
the available expression data
E
to identify the cell lines
C
for which these genes
exhibit a coherent expression (arrow 1). In the next step, the response data
R
are
employed to select drugs
D
that elicit a similar response in these cell lines (arrow 2).
This set of drugs is then utilized to refine the set of cell lines by eliminating those
that have an incoherent response profile and adding others that behave similarly
across these drugs (arrow 3). Finally, this refined set of cell lines is used to probe for
genes that are coexpressed in these lines (arrow 4). This alternating procedure is
reiterated until it converges to stable sets of genes, cell lines, and drugs. We refer to
these sets as comodules
M
GCD
, which generalize the concept of a module from a
single dataset to multiple datasets.