Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
recommended nematicide solution as insurance, but this
will not eliminate nematodes from infected planting
material.
Use a resistant crop in the fallow period to reduce
nematode numbers. In short fallows, Brassica crops can
be grown in the cooler months. For long fallows, use
resistant grasses such as Rhodes grass.
•
Use a recommended herbicide, injected into the old
banana plants before cultivation, to eliminate banana
regrowth and nematode carry over.
•
Monitor nematode damage by assessing root symptoms.
Do this before applying nematicide.
•
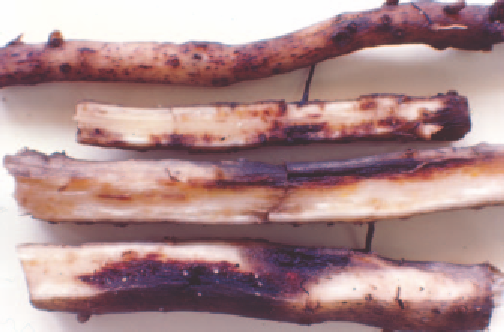
Fig 5.51 Detail of root damage caused by nematodes.
Apply recommended nematicides during the cropping
cycle to reduce crop losses.
•
Apply and conserve organic matter to help suppress
nematode numbers; however, this will not control severe
nematode infestations.
•
VIRUSES
BUNCHY TOP
■
Cause
Banana bunchy top virus
(Babuvirus) .
Symptoms
The most obvious symptom is the development of dark
green f flecks along veins of the leaves producing a
'dot-dash' pattern. This is best seen from the underside of
the leaf at the base of the leaf adjacent to the midrib. The
dark green f flecks in the veins can often be seen 'hooking'
into the midrib from the leaf blade.
Fig 5.52 Nematode root infection is apparent after strong winds.
movement resulting from f floods and water runoff,
adhering to machinery, equipment, workers and animals.
The nematode may survive on weed hosts or volunteer
bananas after infested stools are destroyed.
Infected leaves stand upright and become pale yellow
around the margin, which may be more wavy than normal.
Growth is reduced and the emerging leaves become choked
in the throat of the plant producing a 'bunchy top' effect.
Infected plants are stunted and have vein f flecking in the
leaf sheaths of the pseudostem as well as in the leaves.
Plants infected at an early stage of growth rarely produce
bunches. Those infected later may produce bunches that
project upwards from the throat of the plant rather than
hang. Flecking is frequently seen in the f flower bell.
Importance
Burrowing nematode is a major problem in all production
areas. Cavendish types are susceptible and heavy
infestations can seriously reduce the economic life of
plantations. Banana is also a host of root-knot, root-lesion
and spiral nematodes.
Management
•
Carefully select planting material. Use tissue culture
plants that are free from nematodes or establish planting
material nurseries on clean ground from tissue culture
plants. Planting material can also be dipped in a
Source of infection and spread
The virus spreads from diseased to healthy plants by the
banana aphid (
Pentalonia nigronervosa
). Aphids feeding