Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
consistently at levels that limit production only in specific
areas. These are the Granite Belt (Queensland), Sydney
Basin and Orange (New South Wales), as well as occasional
outbreaks in the variety Pink Lady during wet seasons in
Western Australia.
Alternaria
species are common fungi found in Australian
apple orchards, and the disease could potentially appear
in other states. The presence of Alternaria in an orchard is
not sufficient evidence on its own for the use of control
measures, because environmental conditions play a major
role in determining disease severity. This may explain
occasional reports of symptoms from production areas
such as South Australia and some areas in Victoria, which
normally have low summer rainfall.
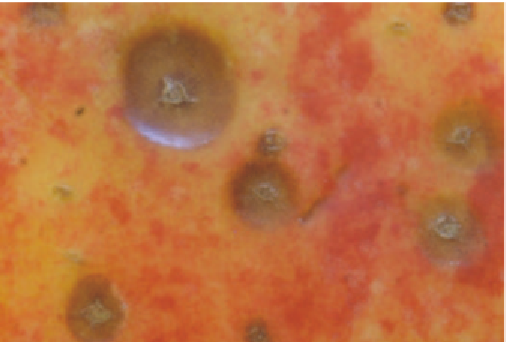
Fig 3.12 Alternaria spot on fruit.
Management
•
This disease should not be confused with Alternaria core
rot, or mouldy core - an internal, postharvest storage rot
caused by
Alternaria alternata
.
Ensure infected leaf material and winter prunings,
especially those with active buds, are completely broken
down, covered or removed from the orchard before the
start of leaf emergence in spring.
Source of infection and spread
Alternaria spores commonly occur in overwintering leaf
and fruit buds, as well as infected leaf litter and buds on
winter prunings. Overwintering leaf litter is thought to be
a significant source of inoculum for new season infections.
Make one or two applications of a broad-spectrum
fungicide as a part of a regular apple black spot spray
program.
•
Once leaf symptoms appear, generally just after mid-
summer rains, apply registered late-season fungicides
to manage symptoms in leaves and fruit.
•
Leaf blotches are almost always observed before the
appearance of fruit spots, and can act as a good indicator
of when to begin late season control measures.
For sites where severe defoliation has occurred in previous
years, apply registered broad-spectrum fungicides after
fruit harvest to reduce premature leaf drop.
•
Warm, wet weather appears to favour disease development.
Apply urea to the trees late in the season to promote
the breakdown of infected apple leaves after natural
leaf fall. Sweep leaves from underneath trees into the
inter-row spaces where they can be further broken
down by mowing. Similarly, put winter prunings in
the inter-row spaces, where they can be broken down
before spring.
•
Importance
Although Alternaria leaf blotch (caused by
Alternaria
species) has been in Australia for many years, the relatively
new disease Alternaria fruit spot has been recorded
BITTER ROT
■
Cause
The fungus
Glomerella cingulata
.
Symptoms
Bitter rot affects both apple and pear.
Symptoms are most evident on fruit, although twigs and
leaves may also be affected. On fruit, small, soft, circular,
light brown, slightly sunken spots develop and enlarge rapidly
to rot large areas of the fruit. Near the centre of each spot
Fig 3.13 Detail of Alternaria spot.